Figure 2.
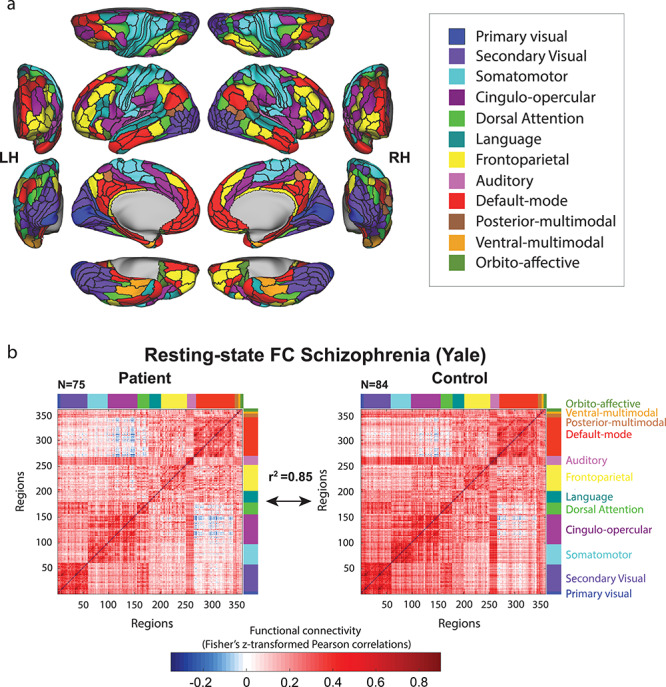
Testing for generalization to a distinct set of regions, network definition. (a) Network partition based on the multimodal parcellation by Glasser et al. (2016). The main parcellation (Fig. 1) used regions defined in terms of voxels, whereas this parcellation is defined in terms of surface vertices. Functional networks were assigned based on the General Louvain method for community detection with resting-state data in healthy adults (Ji et al. 2019). (b) RSFC matrices based on this alternative set of regions and networks were used to replicate the previously found similarity between schizophrenia patients and healthy control subjects. This suggests that the particular choice of regions and networks used for the main analyses did not substantially influence results—that the results are generalizable.
