Figure 4.
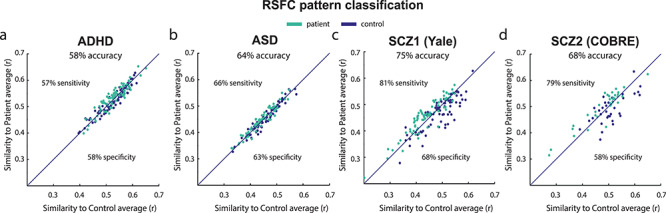
Individual patient-control multivariate classification based on connectome-wide resting-state functional connectivity patterns. Class labels were predicted above chance using a simple classification method in (a) ADHD, (b) ASD and the schizophrenia, (c) Yale, and (d) COBRE datasets. Classifying a subject involved computing that subject’s connectome-wide similarity with the patient-group average and the control-group average, with that subject being assigned to the group with higher similarity. This demonstrated the potential informativeness of whole-brain RSFC similarity in diagnosing individuals, despite overall high similarity between patients and controls at the group level. Note that more complex classifiers might provide better classifications but that straightforward inferences regarding connectome-wide similarity would not be possible with such approaches.
