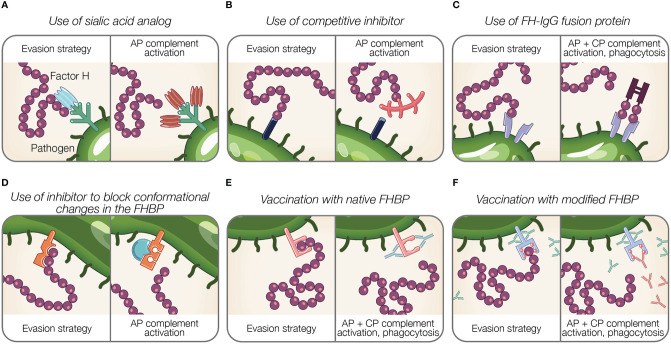
Figure 4.
Potential therapeutic and preventive strategies targeting the interaction between Factor H and pathogens. (A–F) Theoretical representations of pathogen evasion strategies targeted for therapy and prevention are shown. For each box, the left panel illustrates a pathogen evasion strategy and the right panel represents the intended result of therapeutic intervention, which includes AP and CP activation, and phagocytosis. (A) Sialic acid species (shown in light blue) are replaced by analogs unable to recognize FH (shown in brown). (B) Competitive inhibitors for FH binding proteins (FHBP) prevent FH interaction with the pathogen surface. (C) FH fusion proteins containing the Fc portion of IgG fused to FH binding fragments (CCPs 6–7, 19–20) bind FHBP to activate the CP via antibody recognition, facilitate Fcγ receptor-mediated phagocytosis, and prevent FH binding to the pathogen surface. (D) Inhibitors prevent conformational change of FHBP required to enhance their binding to FH. (E) Vaccination with native FHBP. (F) Vaccination with modified FHBP unable to bind FH, reveals FHBP epitopes (red balls) to improve immunogenicity.