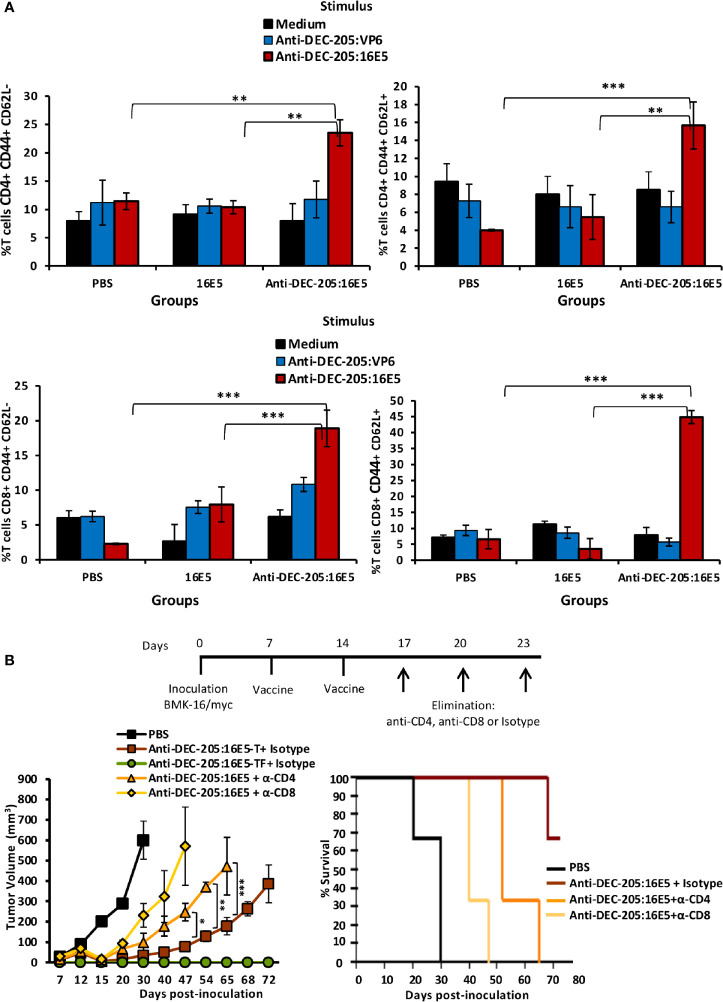
Figure 4.
16E5-specific memory T cells play an important role in protecting against tumor cells. (A) Mice immunization was performed as indicated in Figure 2 with anti-DEC-205:16E5, anti-DEC-205:VP6 or PBS. In vitro antigen stimulation of cells from DLNs and T cell staining was performed as indicated in Figure 3 . The left panels show the percentage of CD4+ CD62L- and CD8+ CD62L- T cells (effector memory) and right panels show the percentage of CD4+ CD62L+ and CD8+ CD62L+ T cells (central memory). Data from one representative experiment (3 mice per group) out of three is shown. (B) Mice were inoculated with 5x105 BMK-16/myc tumor cells and immunized with anti-DEC-205:16E5 or PBS in the presence of Poly I:C, as indicated in Figure 2 . On the indicated days, groups of mice immunized with anti-DEC-205:16E5 were inoculated i.p. with anti-CD4-, anti-CD8 mAbs, or mAb III-10 as isotype control. Tumor growth (left panel) and mice survival (right panel) were followed up for 72 days. In the tumor growth panel, the mice treated with anti-DEC-205:16E5 and the mAb isotype control were divided in mice that developed tumors (anti-DEC-205:16E5-T) and mice that remained tumor-free (anti-DEC-205:16E5-TF). Data from one representative experiment (four mice per group) out of two is shown. Vertical bars indicate standard deviation. Statistically significant differences are represented as p values (*< 0.05; **< 0.01; ***< 0.001).