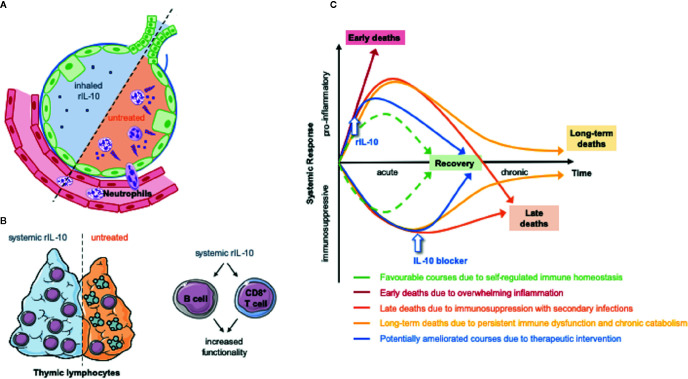
Figure 1.
The effect of therapeutic IL-10 modulation depends on the mode of administration and dynamics. The systemic or local application of recombinant IL-10 have experimentally shown beneficial effects. (A) Inhaled IL-10 attenuated pulmonary inflammation by preventing detrimental neutrophil recruitment into the lung (61, 62, 73). (B) Moreover, IL-10 suppresses thymic lymphocyte apoptosis in sepsis (69) and has stimulatory effects on CD8 T cells (53, 70) and B cells (51, 53). Both modes of application might represent future therapeutic approaches in humans. (C) The dynamics of the immune perturbation in trauma and sepsis was modeled in recent literature (74). In general a time dependent modulation of IL-10 levels might restore immune hemostasis (75–77). Animal models suggest a beneficial effect of early IL-10 application (76) and the correlation of elevated IL-10 levels and injury severity suggests beneficial effects by IL-10-blockage in later phases (31, 45, 78). The figure contains adapted graphics from Les Laboratoirs Servier - Medical Art under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) for non-commercial use. The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/legalcode, last accessed July 30th, 2020.