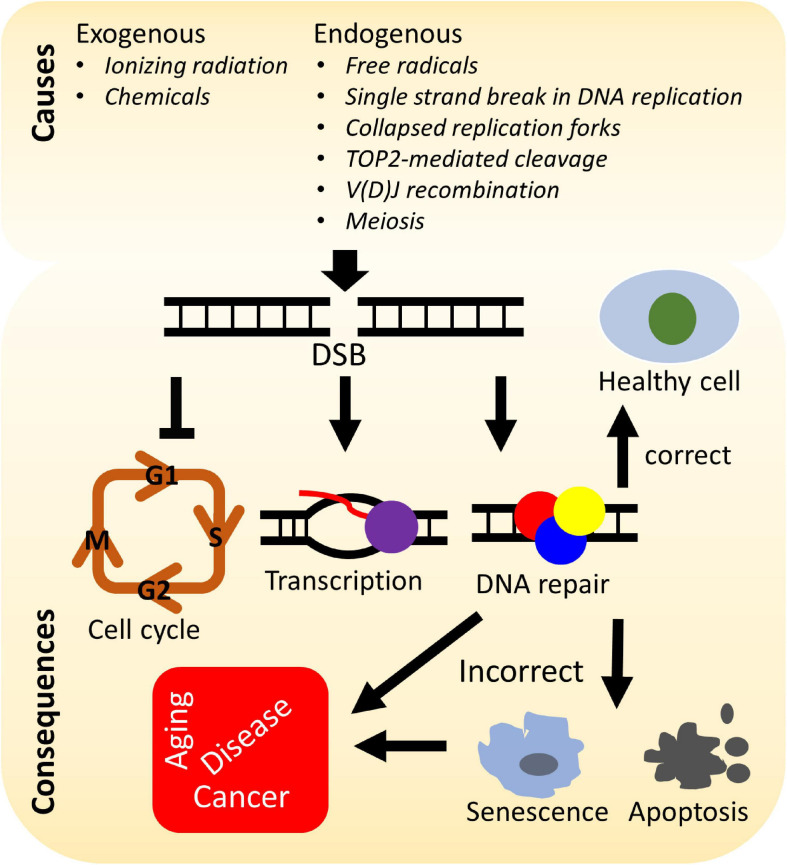
FIGURE 1.
Causes and consequences of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). DSBs arise from various stresses by endogenous or exogenous factors and can lead to arrest of the cell cycle, transcription, activation of the DNA damage response, and repair of the DNA damage. Incorrectly repaired or unrepaired DSBs can result in cellular senescence, apoptosis, premature aging, genetic disorders, and/or tumorigenesis.