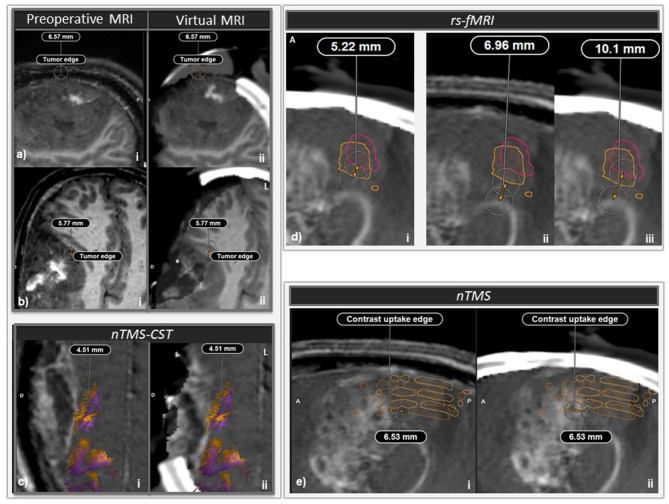
Figure 3.
Intraoperative brain imaging and brain shift correction (BSC). (a) First intraoperative brain CT (iCT) acquisition and BSC, just after dura mater opening. i: sagittal slice of pre-operative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ii: sagittal slice of iCT and elastically transformed pre-operative MRI (virtual MRI) superimposed and coregistered with i. A significant tumor bulge occurred through the craniotomy and a brain shift of 6.57 mm could be measured at some location. (b) Second iCT acquisition with BSC halfway through surgery. i: Axial slice of preoperative MRI, ii: axial slice of iCT with virtual MRI. A 5.77 mm brain shift was measured at the level of the anteromedial edge of the tumor. (c) nTMS-guided corticospinal tract (nTMS-CST) comparison before (orange tracts) and after (purple tracts) BSC. i: Axial slice of preoperative MRI, ii: axial slice of second iCT acquisition with virtual MRI. At some location a 4.51 mm shift was measured between preoperative nTMS-MT before and after BSC. (d) Comparison of rs-fMRI ROIs before (orange outline) and after (pink outline) BSC. i and iii: sagittal slice of second iCT acquisition with virtual MRI, ii: sagittal slice of pre-operative MRI. At some location, a 5.22 mm shift was measured between preoperative rs-fMRI ROIs before and after BSC (i). At some location, the minimal distance between tumoral border and the preoperative rs-fMRI ROI shifted from 6.96 mm (ii) to 10.1 mm after BSC (iii). (e) Sagittal slice of pre-operative MRI (i) and second iCT acquisition with virtual MRI (ii). At some location, a 6.53 mm shift could be measured at some location chosen on the contrast uptake edge of the posterior aspect of the tumor between preoperative MRI and second iCT with virtual MRI. After elastic fusion and virtual MRI, nTMS positive ROIs shifted posteriorly relatively to the tumor.