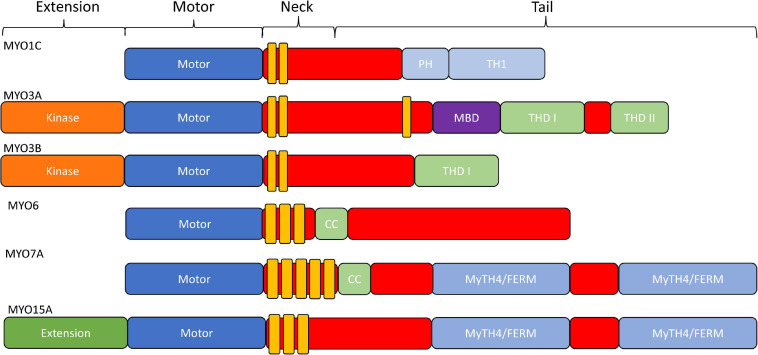
FIGURE 2.
Domain structure of stereocilia-associated myosins. In general, all myosins contain a conserved N-terminal motor domain (head), light chain binding region (neck), and a variable C-terminal domain (tail) which allows specialized functions (e.g., dimerization, filament formation, membrane binding, and cargo/adapter protein binding). Additionally, MYO1C has a membrane binding Pleckstrin-Homology domain, as well as a membrane binding tail homology domain. MYO3A/MYO3B, MYO6, and MYO15A all contain an N-terminal extension domain, with the MYO3A/MYO3B extension being a protein kinase. MYO6 and MYO7A have dimerizing coiled-coil domains, and MYO7A and MYO15A each contain two membrane binding MyTH4/FERM domains.