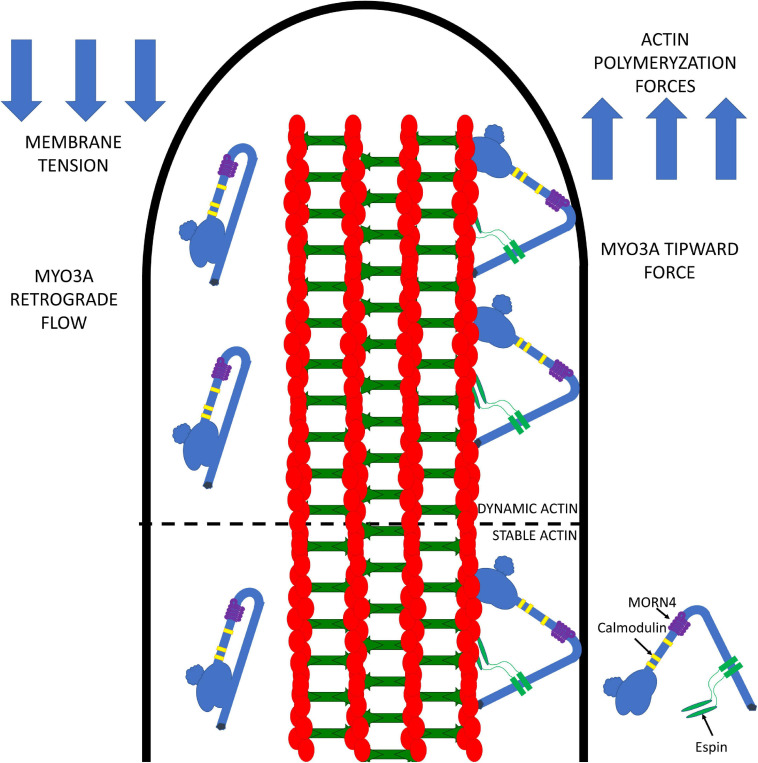
FIGURE 4.
Working model for MYO3A function in inner ear hair cell stereocilia. MYO3A walks toward the plus end of actin protrusions utilizing its motor and actin binding tail domains and can dock at the tips by an unknown mechanism. The tip localized MYO3A can produce an ensemble force that works together with the actin polymerization forces to combat membrane tension, which can result in protrusion elongation or retraction (depending on the balance of forces). The amount of tip-directed force produced by MYO3A motors at the protrusion tips is impacted by the number of motors present, as well as their duty ratio and intrinsic force producing abilities. Examining how MYO3A motor-based forces are altered by physiological factors (e.g., phosphorylation and protein-protein interactions) or disease associated mutations (e.g., deafness mutations) will be the focus of future investigations that will further test this model.