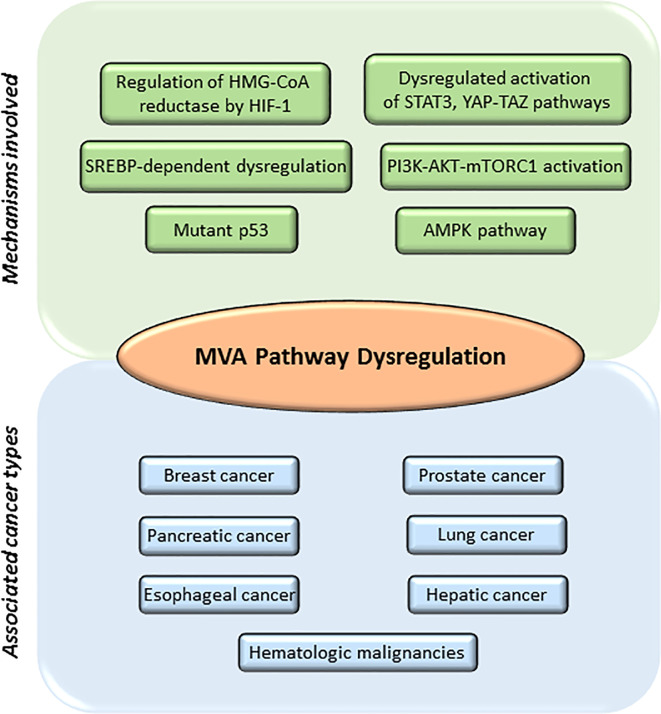
Figure 2.
Main mechanisms involved in mevalonate (MVA) pathway dysregulation and different cancers associated. MVA pathway is upregulated in several cancers including breast, prostate, pancreatic, lung, esophageal, hepatic, and leukemia. Main mechanisms involved in the dysregulation of MVA pathway include: abnormal regulation of the enzyme hydroxy-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR) by different transcription factors such as hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1); mutations or abnormal activation of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs); mutations on tumor suppressor proteins such as tumor protein (p53); decreased AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation; increased activation of signaling pathways such as phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)—protein kinase B (AKT)—mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), Janus Kinase (JAK)/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) or Hippo signaling pathway (YAP-TAZ).