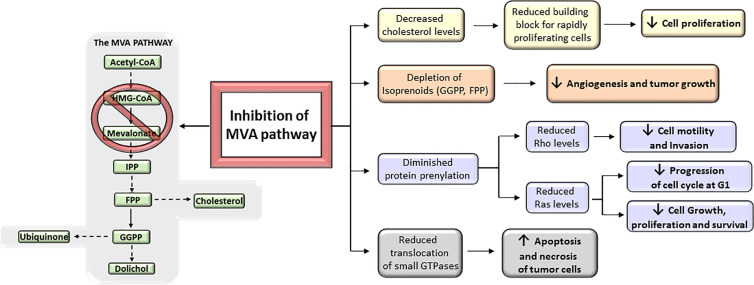
Figure 4.
Antitumoral effects of mevalonate (MVA) pathway inhibition. The inhibition of MVA pathway triggers a series of anticancer events that get to inhibit tumor growth and progression. These include the reduction of MVA synthesis, which in turn decreases the levels of downstream products (isoprenoids) and therefore prevents protein prenylation; the reduction in the translocation of small GTPases such as Rho and Ras to the cell membrane; and the inhibition of cholesterol synthesis. All these inhibitory actions suggest that targeting the MVA pathway could represent a key mechanism to prevent cancer progression.