Figure 6.
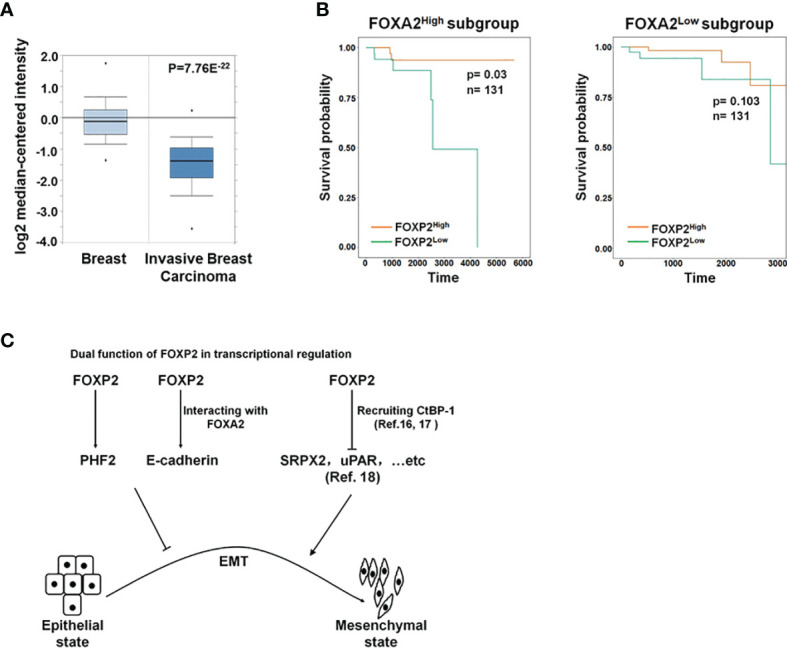
The roles of FOXP2 in EMT of breast cancer cells. (A) The Oncomine boxplots of FOXP2 levels were analyzed between invasive breast tissues and normal breast tissues from the oncomine.org website. The p-value of the TCGA RNA-seq data of normal breast samples (n=61) versus invasive breast carcinoma samples (n=76) was 7.76E-22. (B) The FOXP2-improved survival in breast cancer patients relied on the participation of FOXA2. The FOXA2High subgroup (n=131) or the FOXA2Low subgroup (n=131) contained either the top 1/3 or the bottom 1/3 of the collected BRCA data set (n=394), respectively. FOXP2-related survival of patients in the FOXA2High and FOXA2Low subgroups was fitted by the “survfit” function, and Kaplan–Meier curves were drawn by the “ggsurv” function in the R package “survival”. (C) The roles of FOXP2 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of breast cancer cells. FOXP2 prevented EMT of breast cancer cells by regulating the transcription of multiple EMT-related genes: FOXP2 could bind to certain promoters and stimulate the transcription of genes such as PHF2 and E-cadherin. The transcriptional activation by FOXP2 could be mediated by FOXA2. FOXP2 could also repress the transcription of certain genes such as SRPX2 and uPAR, through recruiting co-repressors such as CtBP-1.
