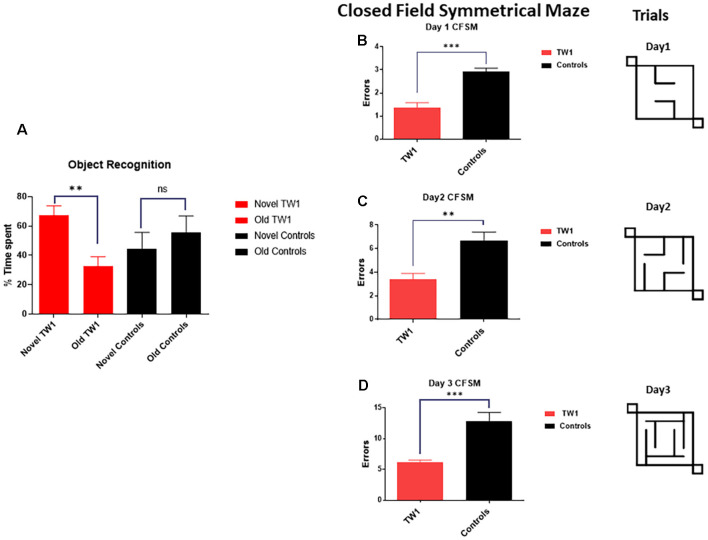
Figure 4.
Passive immunotherapy with the TW1 antibody improves cognitive tasks in the hTau/PS1 Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mice model. Panel (A) shows working memory improvement using a short-term memory test (Novel Object Recognition Test). The bars depict the percentage of the amount of time spent with the novel or old object. Mice treated with TW1 spent more time with the novel object compared to the old object (two-tailed t-test, **p = 0.0019). Vehicle treated mice showed no significant difference in spent with the novel object. Panels (B–D) shows results on the Closed field Symmetrical Maze comparing TW1 treated mice vs. vehicle-treated mice: (B) Day 1 two-tailed t-test ***p < 0.0001; (C) Day 2 two-tailed t-test ** p = 0.0015; (D) Day 3 two-tailed t-test ***p = 0.0002). ns: not significant.