Figure 2.
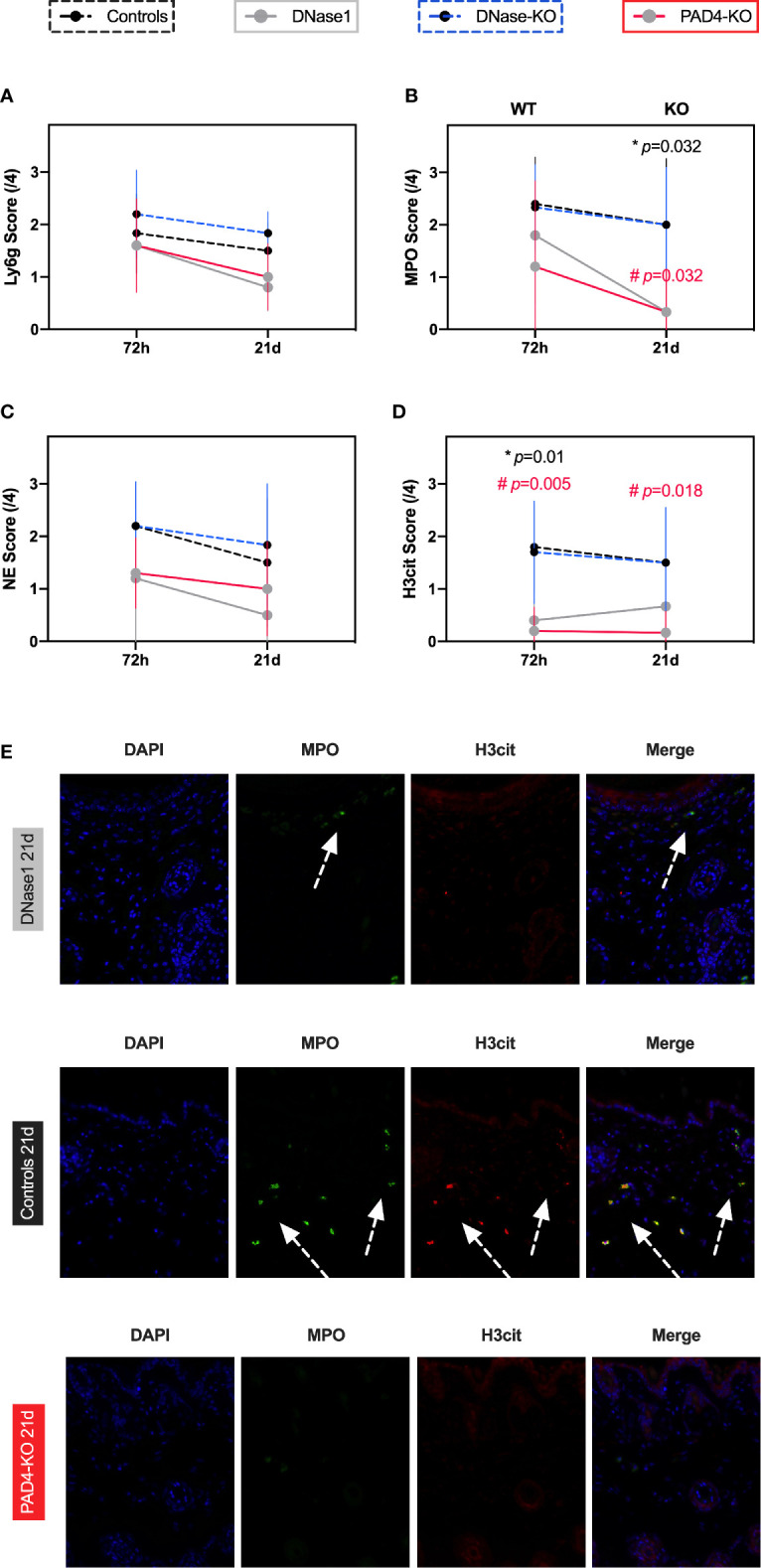
Therapeutic targeting of NETs formation results in decreased neutrophil activation and NETs formation in a model of primary intention wound healing. (A) Ly6G a marker of granulocytes was not affected by genetic alterations of NETs formation or DNase1 treatment. (B–D) Neutrophil activation and NETs formation was significantly reduced by DNase1 treatment or genetic knockout. (E) Representative immunofluorescence images. DNase1 treatment vastly reduced neutrophil activation (MPO) and NETs formation (H3cit). Data shown as Mean ± SD. Comparison was performed always in comparison with controls. Statistics: mixed-effect model with Geisser-Greenhouse correction as well as Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. *DNase1 vs. controls. #PAD4-KO vs. controls.
