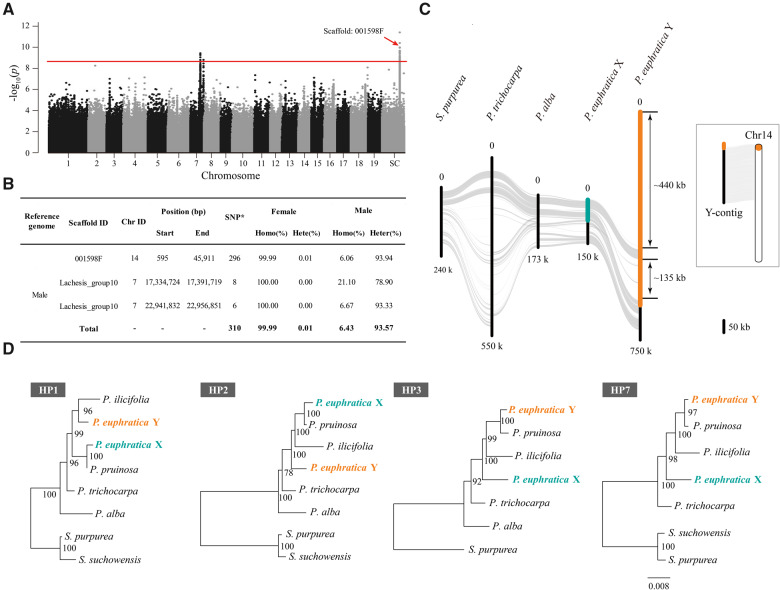
Fig. 1.
XY sex determination on chromosome 14 in Populus euphratica. (A) Manhattan plot of P. euphratica based on the results of genome-wide association study (GWAS) with the male genome as reference. The y axis represents the strength of association (−log10(P value)) for each SNP sorted by chromosomes and scaffolds (SC; x axis). The red line indicates the significance after Bonferroni multiple testing correction (α < 0.05). Note that the scaffold “001598F” is located on chromosome 14 based on its syntenic relationship with the proximal end of chromosome 14 of P. trichocarpa. (B) Summary of male P. euphratica genome regions containing SNPs significantly associated with sex. “SNP*,” significantly associated SNPs; “Homo,” Homozygous; “Hete,” Heterozygous. (C) Synteny relationships between our assembled Y-contig and X chromosome of P. euphratica, as well as the corresponding region of chromosome 14 for P. alba, P. trichocarpa, and Salix purpurea. The highlighted part represents the sex-determination region (SDR), yellow for Y-SDR and green for X-SDR. Schematic diagram showing the corresponding position of the SDR on chromosome 14 of P. euphratica. (D) Phylogenetic relationships of the homologous pairs (HP) shared between Y- and X-SDR of P. euphratica and their orthologous genes in other Salicaceae species. Detailed information about these genes is listed in supplementary table S7, Supplementary Material online and additional phylogenetic trees are shown in supplementary figure S7, Supplementary Material online. Note that only the orthologous genes located on the corresponding region of chromosome 14 were used for phylogenetic analysis.