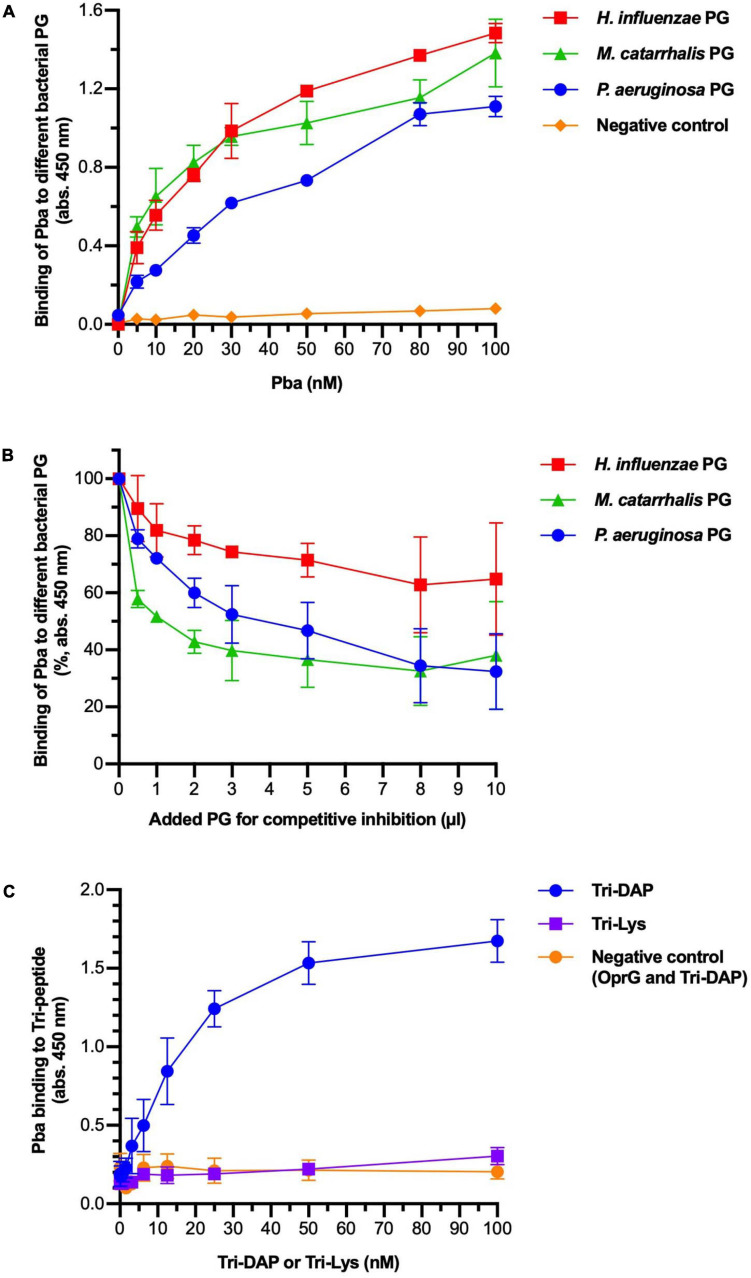
FIGURE 2.
Peptidoglycan-binding anchor (Pba) binds to diaminopimelic acid (DAP) in the peptidoglycan (PG) peptide chain. The interactions between Pba and PG or PG components were analyzed by ELISA. (A) Peptidoglycans from three different Gram-negative bacterial species (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis) were extracted and immobilized in 96-well plates. Recombinantly expressed 6 × His-tagged Pba or OprG (negative control) was added at increasing concentrations. Bound ligands were detected by HRP-conjugated anti-6 × His polyclonal antibodies (pAbs). (B) In a competitive inhibition ELISA, the PG was coated to the wells as above. Pba (50 nM) was preincubated with soluble PG at increasing concentrations before the addition of the mixture to the wells. Since the molarity of the PG sacculi could not be reliably determined, the volume of PG used for preincubation is indicated on the x-axis. Data are presented as absorption at 450 nm of initial value. To detect the binding of Pba to DAP, Tri-DAP (Ala-Glu-DAP), or Tri-LYS (Ala-Glu-Lys) was covalently bound to Sepharose beads, followed by a bead-based ELISA with Pba or OprG (negative control) as ligand (C). The mean and standard deviations are plotted in all graphs, with data from three independent experiments.