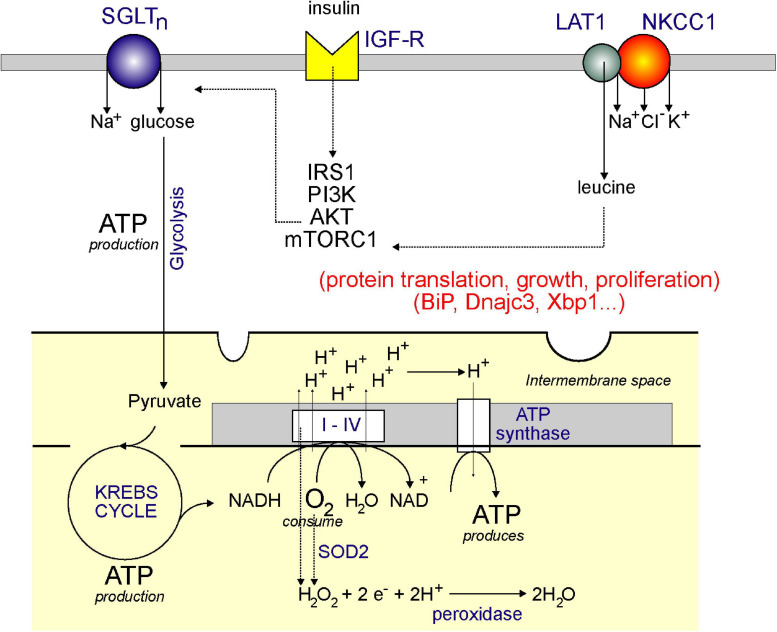
FIGURE 4.
Model showing plasma membrane NKCC1 and mitochondrial respiration: a link through leucine? Aerobic respiration utilizes the KREBS cycle and the electron transport chain. Through the consumption of oxygen (O2) and NADH (produced by the KREBS/TCA cycle), complexes I–IV produces a proton (H+) gradient in the inner membrane of the mitochondria, which is then used by ATP synthase to produce ATP. The KREBS or TCA cycle is powered by pyruvate which comes from glucose through the process of glycolysis. The glucose comes from uptake at the plasma membrane through a Na+-driven glucose transporter. Glucose transport is facilitated by activation of the IGF-R receptor by insulin and stimulation of the IRS1/PI3K/AKT pathway. AKT also stimulates mTORC1, which stimulates protein translation, thereby facilitating cell growth and proliferation. mTORC1 is also stimulated by leucine which enters cells through the LAT1 transporter – which requires interaction with NKCC1. Note that mitochondrial respiration also produces hydrogen peroxide (through complexes I–IV and through SOD2), which can be converted to water by peroxidases.