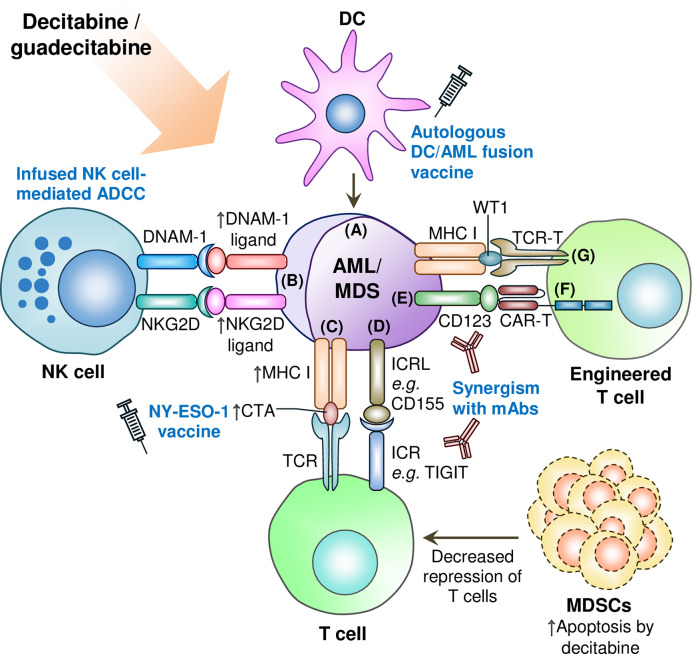
Figure 2.
Synergism of decitabine or guadecitabine with antileikemic immune cells and engineered T cells, and depletion of immunosuppressive cells in AML or MDS microenviroment. (A) DC/AML vacinne combined with decitabine or guadecitabine treatment induces leukemia-specific immunity; (B) Decitabine potentiates infused NK cells’ antileukemia activity by upregulating ligands for NKG2D and DNAM-1 immunoactivating receptors on NK cells. Decitabine combined with anti-CD33 mAb also augments the expression of NKG2D ligands in AML cells; (C) Upregulation of CTA expression such as NY-ESO-1 by decitabine or guadecitabine treatment synergizes with NY-ESO-1 cancer vaccine treatment; (D) Combination of decitabine or guadecitabine with novel immune checkpoint blockade therapy such as anti-TIGIT therapeutic antibody to circumvent resitance of AML or MDS cells to either hypomethylating agent; (E) Potential synergsim of decitabine or guadecitabine with anti-CD123 therapeutic antibody (e.g. tagraxofusp) to induce antileukemic immunity; (F) Decitabine treatment synergizes with CD123 CAR-T cells against AML cells; (G) Potential synergism of decitabine or guadecitabine with WT-1 specific TCR-T cells. ADCC: Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; AML: Acute myeloid leukemia; CAR-T: Chimeric antigen receptor-engineered T cell; CTA: Cancer/testis antigen; DC: Dendritic cell; DNAM-1: DNAX accessory molecule-1; ICR: Immune checkpoint receptor; ICRL: Immune checkpoint receptor ligand; mAb: Monoclonal antibody; MDS: Myelodysplastic syndromes; MDSC: Myeloid-derived suppressor cell; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; NK: Natural killer; NKG2D: Natural killer group 2D; TCR: T cell receptor; TCR-T: T cell receptor-engineered T cell; TIGIT: T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains; WT1: Wilms’ tumor 1. Upward arrow denotes upregulated expression, increased CTA presentation, or induced apoptosis of MDSCs.