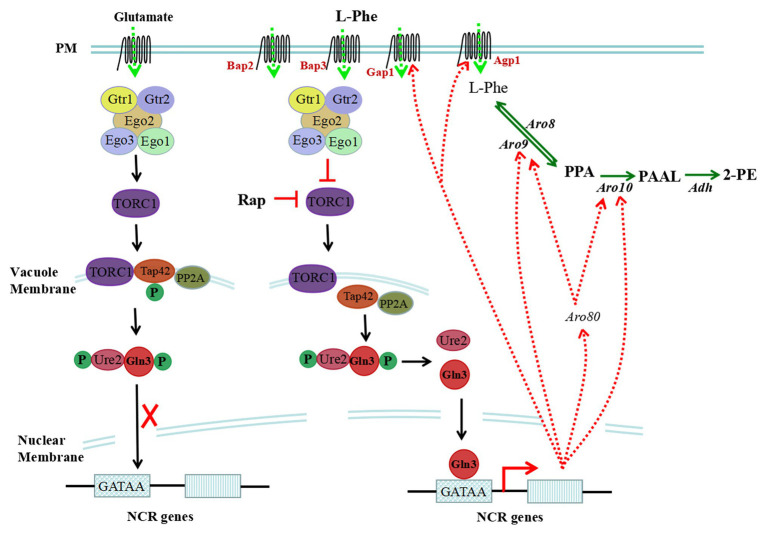
Figure 2.
Sensing and regulation of intracellular L-Phe levels through the target of rapamycin (TOR) pathway. The TOR signalling cascade includes the EGOC complex, TOR complex 1 (TORC1), and downstream effectors (Tap42-PPase and Sch9). Intracellular L-Phe is sensed by the EGOC complex, and TORC1 can be inhibited. However, upon rapamycin treatment or in the presence of a poor nitrogen source, the activity of TORC1 can be restrained, which results in the dephosphorylation of Tap42, freeing it from the vacuole membrane. Gln3 is dephosphorylated by freed Tap42 and is freed from Ure2; then, it targets the nucleus and binds to the GATAA/G motif of nitrogen catabolite repression (NCR)-sensitive genes, activating the transcription of NCR-sensitive genes. In the presence of glutamate, TORC1 is activated and Gln3 cannot be dephosphorylated and resides in the cytoplasm, which represses the expression of NCR-sensitive genes.