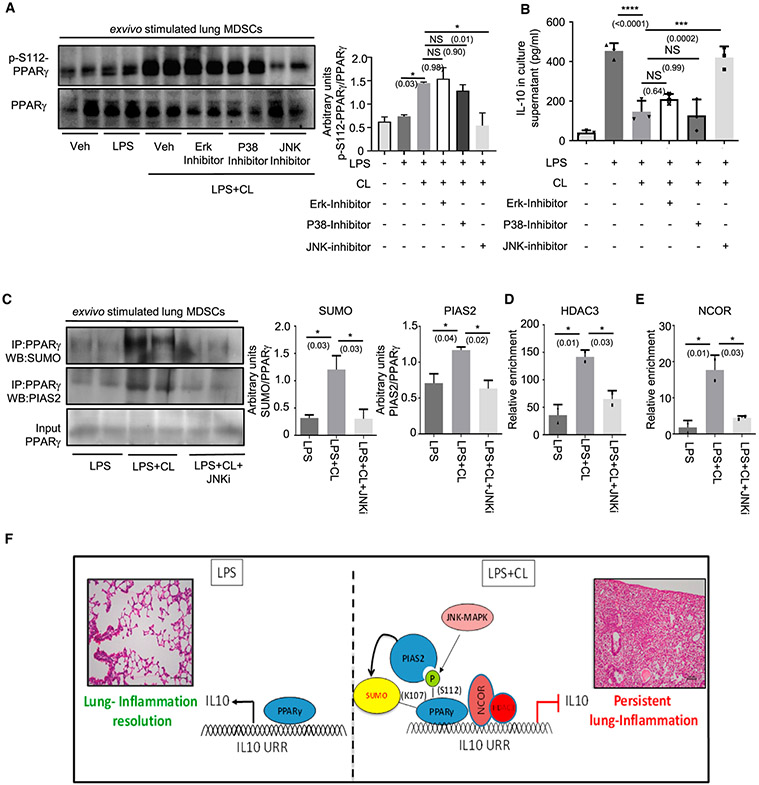
Figure 3. JNK is required for CL-mediated PPARγ S112 phosphorylation.
Lung MDSCs were enriched from C57BL/6 mice of 8–10 weeks of age, seeded at appropriate densities, and stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) ± CL (10 μg/mL) for 3 h, in combination with different MAPK inhibitors, as mentioned.
(A and B) PPARγ S112 phosphorylation studied by western blot analysis after 3 h of stimulation (A). Quantitative densitometry is shown alongside (B) IL-10 in culture supernatant measured by ELISA after stimulation of cells for 6 h.
(C–E) Cells were stimulated for 3 h with LPS ± CL in combination with JNK MAPK-inhibitor.
(C) PPARγ SUMOylation studied by immunoprecipitation followed by western blot analysis using anti- SUMO1 and anti-PIAS2 antibody, respectively. Densitometry analysis is plotted in the right panel.
(D) HDAC recruitment to IL-10 promoter investigated by ChIP assay.
(E) NCOR recruitment to the IL-10 promoter investigated using ChIP assay.
(F) Diagrammatic representation showing the possible mechanism of CL-mediated IL-10 suppression, based on the results of this study.
Experiments were conducted with 2–3 replicates in each group. The data shown are means ± SDs and representative of 2 independent experiments. Statistical significance was calculated using 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Each dot on the plots represents a biological replicate. The numbers in parentheses indicate the respective p values for statistical significance between the marked groups. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; NS, not significant. See also Figure S3.