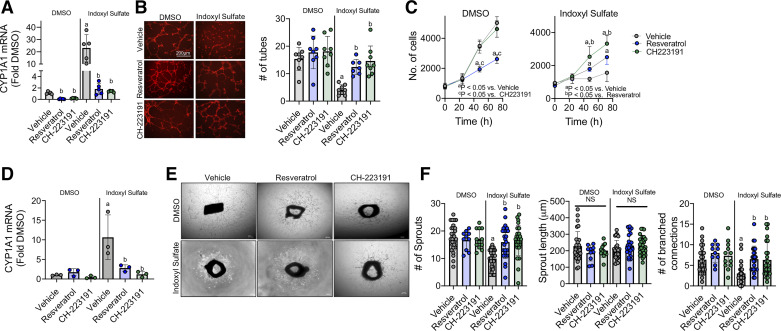
Figure 3.
Pharmacological antagonism of AHR attenuates IS impairments in angiogenesis. A: mRNA quantification of CYP1A1 levels (index of AHR activation) with 25 µM resveratrol or 1 µM CH223191 in HUVECs (n = 5/group). B: representative images and quantification of endothelial cells tube formation with either IS or DMSO with or without the AHR antagonists (n = 7–8/group). Scale bar = 200 µm. C: quantification of endothelial cell proliferation following treatment with IS or DMSO coincident with either resveratrol or CH223191 (n = 12/group). D: quantification of CYP1A1 mRNA levels in aortic rings treated with either DMSO or indoxyl sulfate with or without AHR antagonism (n = 3/group). E: representative phase-contrast images of aortic rings treated with AHR antagonists alongside with DMSO or IS. Scale bar = 0.01 inches. F: quantification of total sprouts, mean sprout length (µm), and number of branch connections from aortic ring experiments (n = 10–17/group). aP < 0.05 vs. DMSO (within treatment), bP < 0.05 vs. Vehicle (within group—DMSO or IS) using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc testing. Error bars = SD. AHR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; IS, indoxyl sulfate; HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells.