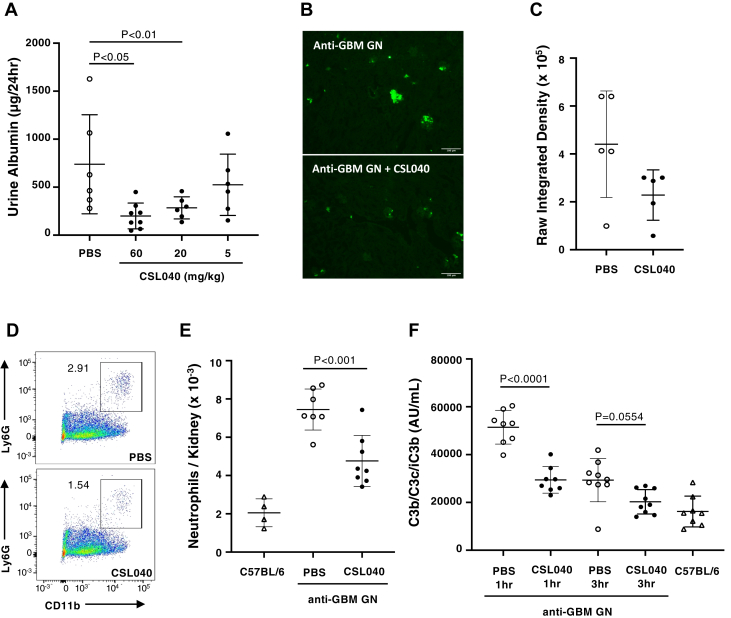
Figure 7.
The effect of CSL040 in an attenuated-passive anti-GBM glomerulonephritis mouse model. Glomerulonephritis was induced in C57BL/6 mice by i.v. injection of rabbit anti-GBM polyclonal antibody followed 6 days later by i.p. administration of MsαRb antibody. CSL040 (filled circles) or a PBS control (open circles) was given by i.p. administration 1 h prior to MsαRb. Naive C57BL/6 mice (open triangles) were used as an additional control. Urine was collected using metabolic cages, and mice were sacrificed after 24 h (for albuminuria and complement deposition) or 1 to 24 h (neutrophils staining in kidneys and measurement of plasma complement components). N = 6 to 8 per group. A, urine albumin levels in mice treated with PBS or CSL040 at 5, 20, or 60 mg/kg. B, intraglomerular infiltration of neutrophils 3 h after MsαRb administration was diminished by 60 mg/kg CSL040 as shown by the representative images of immunofluorescence staining of mouse kidneys (magnification 100×; the bar represents 100 μm). C, quantification of raw integrated density. D, infiltrating neutrophils in kidney were quantified by flow cytometry using the Ly6G and CD11b markers. The number next to the gate (outlined with a box) is neutrophils as a percentage of CD45+ cells in the plot of one representative mouse. E, neutrophil numbers from mice in each group were calculated from flow cytometry. F, effect of PBS or CSL040 (60 mg/kg) treatment on the plasma levels of complement activation fragment C3b/C3c/iC3b after induction of glomerulonephritis. Data shown are mean ± SD. Statistically significant differences in values between groups were calculated using ordinary one-way ANOVA with the Tukey's test for multiple comparisons. GBM, glomerular basement membrane; GN, glomerulonephritis.