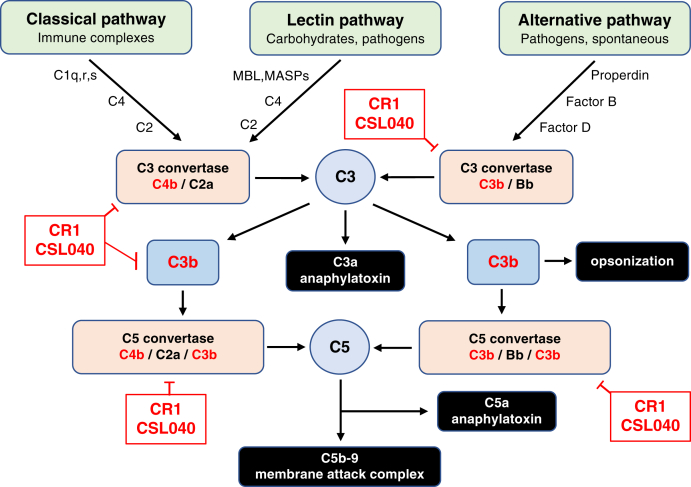
Figure 8.
Involvement of CR1/CSL040 in complement pathway inhibition. The three pathways of the complement systems are the classical, lectin, and alternative pathways, each activated by specific mechanisms. All pathways converge at the level of C3 before diverging to form the key complement end products: the C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins that mediate inflammatory processes; the opsonin C3b; and the lytic membrane attack complex. The activated fragments of C3 and C4, C3b and C4b, are key components in all three complement pathways, and CR1/CSL040 (red boxes) can bind both C3b and C4b, thereby inhibiting further complement activation. One mechanism is via CR1/CSL040 displacement of C2a or Bb in the C3 and C5 convertases (decay acceleration); the other is promotion of factor I-mediated cleavage of C3b/C4b into inactive fragments (cofactor activity). CR1, complement receptor 1.