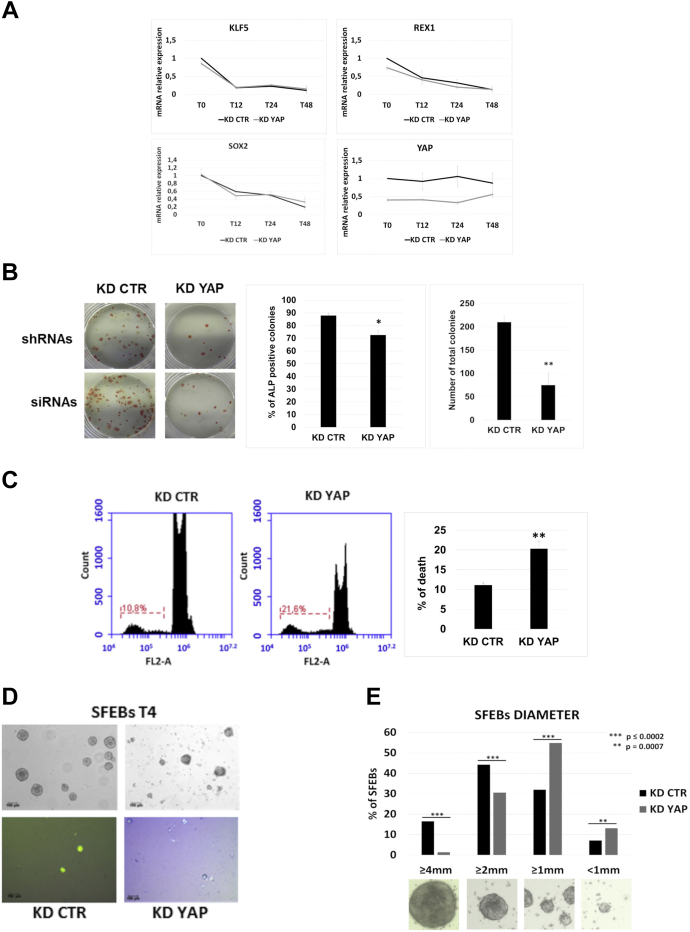
Figure 2.
The KD of YAP does not impair the pluripotency of ESCs but decreases cell viability.A, quantitative PCR analysis of stemness marker genes upon leukemia inhibitory factor withdrawal in KD YAP compared with KD CTR cells. For each data set, n = 3. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. B, representative images of alkaline phosphatase (AP) staining at day 7 upon transfection of siRNAs. YAP KD causes a significant (∗∗p < 0.01) decrease in the number of total AP colonies, whereas the percentage of AP-positive colonies seems to be almost unaffected (∗p < 0.05) with respect to CTR KD cells. For each data set, n = 3. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. C, representative flow cytometry histograms of gated nuclei fluorescence (propidium iodide staining) detected using the FL2 (480 nm) photodetector (FL2-A). YAP KD significantly (∗∗p < 0.01) increases the percentage of sub G0/G1 cell population, compared with KD CTR, n = 3. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. D, representative images of KD CTR and KD YAP SFEBs tested with trypan blue exclusion assay. The scale bar represents 100 μm. E, statistical analyses of the dimensions of SFEBs from YAP KD compared with CTR KD cells. Diameter measurement was performed using ImageJ 1.52v software. For each data set, 300 SFEBs from each biological triplicate were analyzed. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. CTR, control; KD, knockdown; SFEBs, serum-free embryoid bodies; YAP, Yes-associated protein.