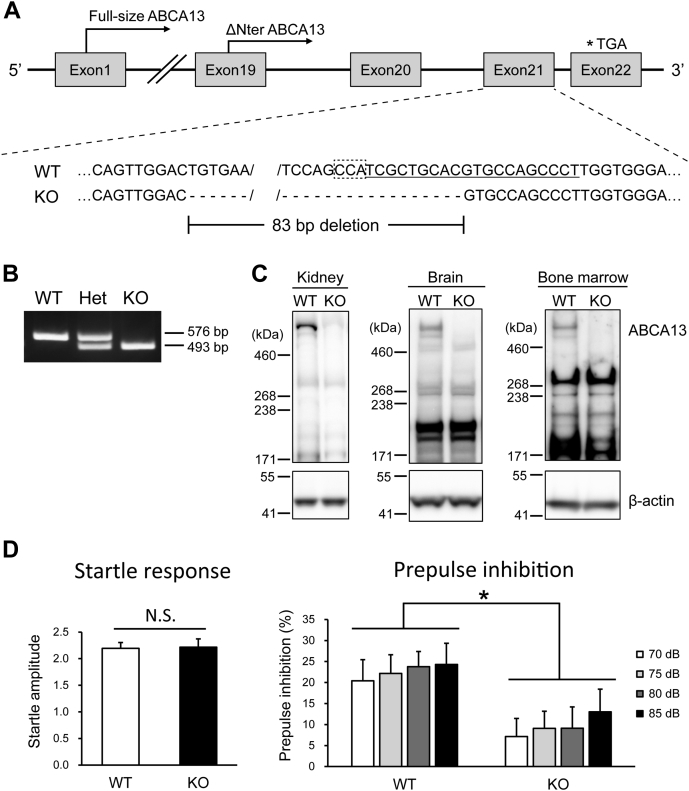
Figure 5.
Generation and prepulse inhibition of Abca13 KO mice.A, schematic representation of Abca13 KO mice generation by the CRISPR/Cas system. A schematic of the Abca13 gene locus with the genomic sequences of WT (upper) and KO (lower) mice is shown. The sgRNA sequence is underlined, and the PAM sequence is indicated by the dotted box. Exons are indicated by boxes, and introns are indicated by lines. The asterisk indicates the stop codon by 83 bp deletion. The translation start sites for full-size ABCA13 and ΔNter ABCA13 are indicated by the arrows. B, a representative result of genotyping PCR with genomic DNA from WT, Abca13 heterozygous KO, and homozygous KO mice. C, Western blot analysis of the kidney, brain, and bone marrow cells from WT and Abca13 KO mice using anti-ABCA13 antibody. β-actin was used as a loading control. D, acoustic startle response for 120 dB (left) and prepulse inhibition for 70–120, 75–120, 80–120, and 85–120 dB (right) in WT and Abca13 KO mice. Data are shown as means + S.E.M. (WT, n = 16; KO, n = 15). ∗p < 0.05 compared with WT mice.