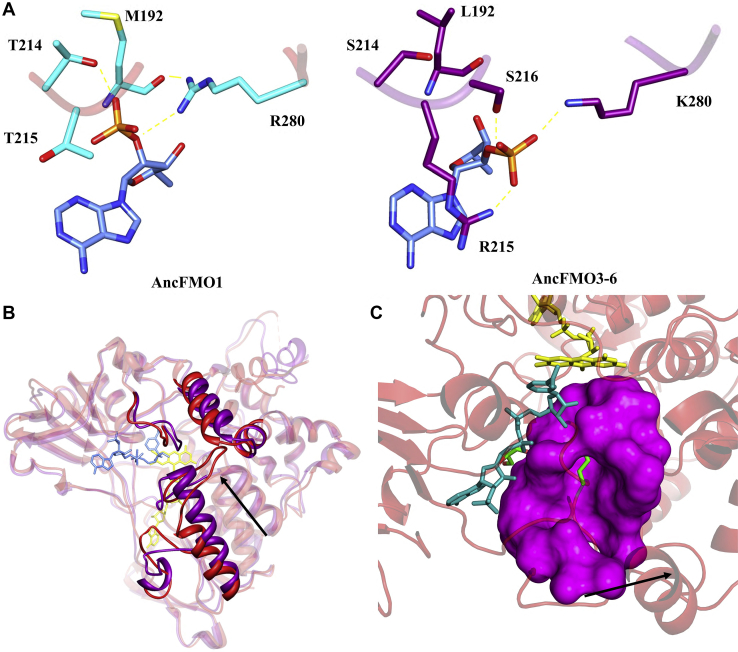
Figure 5.
Unique structural features of AncFMO1.A, the differing 2’-phosphate binding site of NADP+ for AncFMO1 (left, side chains in cyan) compared with AncFMO3-6 (PDB:6SE3) (right, side chains in dark purple) is shown with key hydrogen-bonding interactions shown as yellow dashed lines. NADP+ is shown in cornflower blue. B, the conformation adopted by residues 416 to 425 that reaches out toward the α-helical triad in a large arched conformation is indicated by the black arrow. Super positioning AncFMO1 (red) against AncFMO3-6 (dark purple) conveys the new structural topology. C, the large active site cavity (approximately 19 Å wide) is depicted in magenta and stretches out toward the solvent and the membrane–protein interface (indicated with a black arrow). The side chain of E281 is shown in green pointing toward the isoalloxazine ring and the active site. FAD, NADP+, and glycerol molecules are shown in yellow, cornflower blue, and green, respectively. AncFMO, ancestral flavin-containing monooxygenase; FAD, flavin adenine dinucleotide.