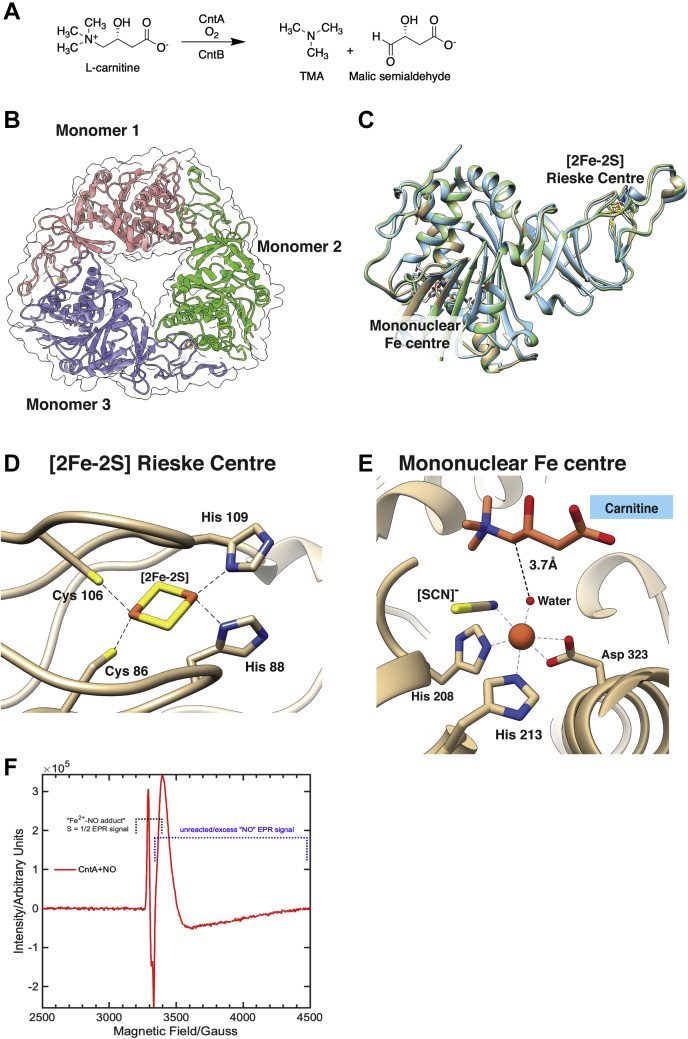
Figure 1.
The overall structure of CntA and its catalytic center.A, the reaction of carnitine oxidation by CntAB to trimethylamine (TMA) and malic semialdehyde. B, CntA depicted as a homotrimer with the secondary structure represented in a ribbon depiction in a translucent overall surface representation with each monomer in blue, red, and green, respectively. C, an overlap of three monomer structure units (apo, carnitine bound, gBB bound), showing no major changes to the tertiary structure of CntA with and without ligands bound. The C and N labels refer to the sequence termini. The Rieske center and the mononuclear Fe center are 44 Å apart in the same subunit. D, the Rieske center in CntA is coordinated by Cys86, Cys106, His88, and His109. E, the catalytic mononuclear Fe center in CntA is coordinated by a His-His-Asp catalytic triad (His208, His213, Asp323), a water, and thiocyanate ion. Carnitine is shown above the mononuclear Fe center with a distance from the water molecule to the site of substrate cleavage. F, electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectrum of as-isolated CntA in the presence of nitric oxide (NO), showing the EPR-active, S = ½ species due to the formation of Fe2+-NO adduct. EPR conditions: microwave power 30 dB, modulation amplitude 5 G, time constant 81 ms, conversion time 41 ms, sweep time 84 s, receiver gain 60 dB, microwave frequency 9.384 GHz, temperature 20 K.