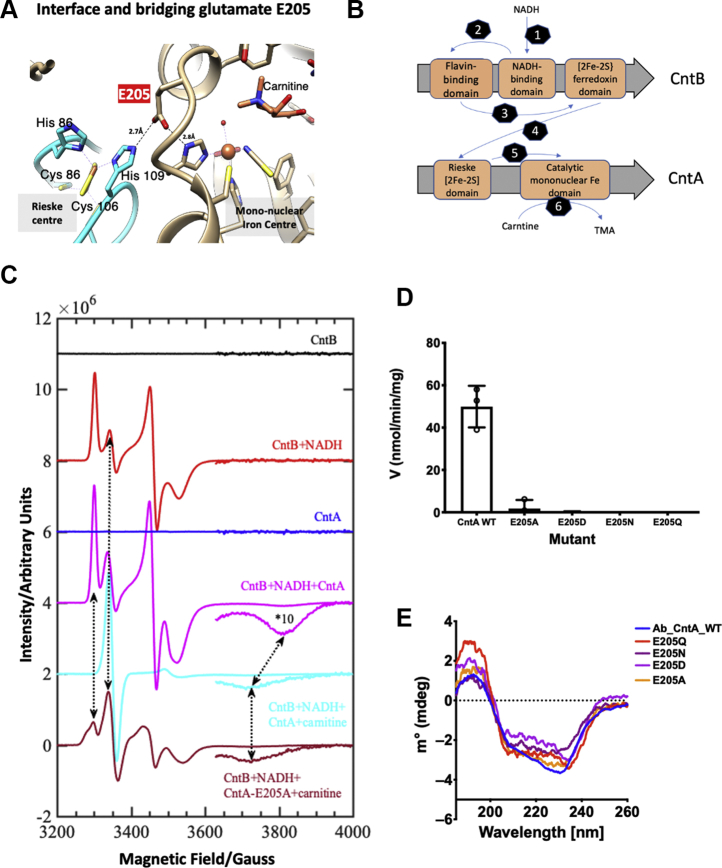
Figure 2.
Structural basis of intersubunit electron transfer and investigations by EPR.A, electron transfer in CntA between the Rieske center and the mononuclear Fe center across the interface of two neighboring CntA subunits (colored in cyan and brown, respectively) involved a key bridging glutamate reside (E205). Distances shown in angstrom. B, proposed electron transfer pathways from the reductant NADH to the catalytic mononuclear Fe center in CntA via the reductase CntB. C, EPR spectra of a series of combinations of WT CntAB proteins, E205A mutant, NADH, and L-carnitine to track the propagation of EPR signal and thus the inter-/intrasubunit electron transfer. NADH reduction in CntB (black trace to red trace; steps 2 and 3 in B); the EPR active [2Fe-2S]+1 species in the CntA Rieske center with and without carnitine present (red trace to magenta trace and cyan trace; steps 4–6 in B). The E205A mutant (wine red trace) demonstrates an EPR signal different from that of the wildtype CntA (cyan trace), indicating a disruption to the electron transfer pathway; EPR conditions, as described for Figure 1F. D, Activity assays of CntA E205 mutants. E, circular dichroism measurement comparisons between CntA wildtype and E205 mutant enzymes showing no difference in secondary structure.