Figure 4.
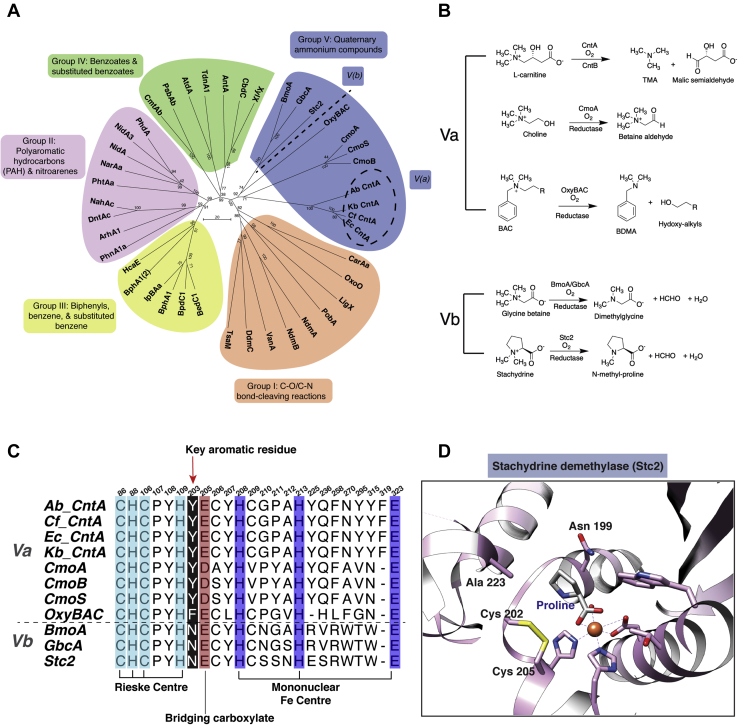
CntA represents a novel group of Rieske oxygenases using quaternary amine substrates (group V).A, phylogeny of Rieske oxygenases showing the five distinct groups. The evolutionary history of Rieske oxygenases was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method in MEGA7 (68). The dashed circle grouping shows the clustering of CntA including Acinetobacter baumannii (Ab), Escherichia coli SE11 (Ec), Klebsiella pneumonia (Kb), and Citrobacter freundii (Cf) (see supplementary information, Appendix 1 for a list of gene accession ID’s). Group V Rieske oxygenases oxidize quaternary amine substrates, including carnitine (CntA), choline (CmoA/B/C), benzalkonium (OxyBAC), glycine betaine (BmoA, GbcA), and stachydrine (Stc2). B, chemical reactions catalyzed by Rieske enzymes from the Group V Rieske oxygenases involved in quaternary amine oxidations. Group Va includes carnitine oxygenase (CntA) choline monooxygenase (CmoA, CmoS, and CmoB), and benzalkonium oxygenase (OxyBAC). Group Vb carries out oxidative demethylation reactions. C, sequence alignment of the substrate-binding pocket residues of group V Rieske oxygenase involved in quaternary amine oxidation. The aromatic residues for substrate coordination through a π–cation in group Va and the corresponding position in group Vb are highlighted by a red arrow. The Rieske center is coded in blue, the catalytic triad of the mononuclear Fe center is shown in purple, and the bridging carboxylate is highlighted in pink. D, the substrate-binding site of the group Vb quaternary amine degrading enzyme Stc2. The substrate mimics proline in Stc2 coordinates with the catalytic mononuclear Fe center via a carboxylic acid group.