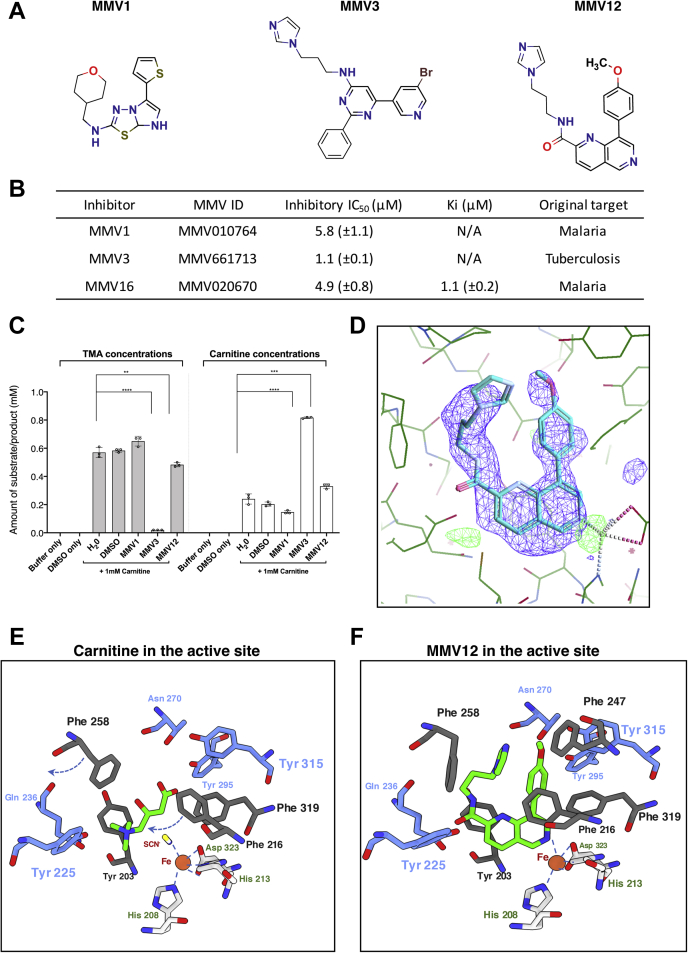
Figure 6.
Structural basis of CntA inhibition.A, chemical structures of the three CntA inhibitors: (MMV1), MMV010764 (N-[(oxan-4-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[2,1-b][1,3,4]thiadiazol-2-amine); (MMV3), MMV661713(6-(5-bromopyridin-3-yl)-N-[3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propyl]-2-phenylpyrimidin-4-amine); (MMV12), MMV020670 (N-[3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propyl]-8-methyl-1,6-naphthyridine-2-carboxamide). B, summary of the inhibitor assays with inhibitory IC50 data values shown for n = 3 replicates. C, evaluation of CntA protein inhibitors (MMV1, MMV3, MMV12) using A. baumannii bacterial cultures. Cells treated with inhibitors MMV3 (p < 0.0001) and MMV12 (p < 0.001) caused significant reduction in trimethylamine (TMA) formation from carnitine, whereas MMV1 did not reduce TMA production. Carnitine was added to a final concentration of 1 mM prior to the incubations with/without additional inhibitors. Control runs of buffer only and DMSO only did not have carnitine in the treatment, and no TMA was observed. N = 3 for all conditions. Statistics was carried out using one-way ANOVA. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. D, A Polder OMIT map (blue) of MMV12 (MMV020670) displayed at 3.0σ in the CntA active site. E–F, comparison of selected residues in the CntA active site interacting with the carnitine substrate and MMV12 (MMV020670) inhibitor. Polar interacting residues (magenta) remain unchanged, whereas for the hydrophobic π–π interacting residues (dark gray), positional changes for Phe258 and Phe216 as indicated by dashed arrows in E.