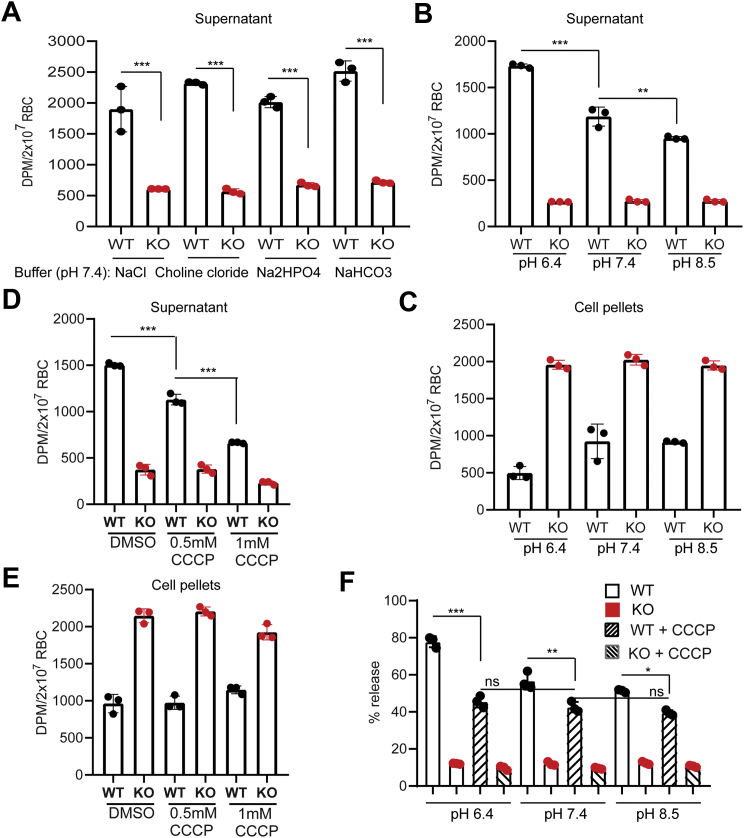
Figure 4.
Proton gradient affects S1P export activity in RBC. A, transport activity of S1P in WT and Mfsd2b KO red blood cells (RBCs) at indicated buffers. Removal of sodium or chloride does not affect S1P export activity. B, C, effects of pH levels on S1P release from WT RBC. We noted that S1P synthesis in WT and KO RBCs in the pHs was unchanged. A lower pH increases and higher pH decreases the release of S1P. D, E, effects of CCCP (carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone) on S1P release from WT and KO RBCs at pH 7.4. F, effects of CCCP on S1P release from WT and KO RBCs at indicated pHs. In these experiments, wildtype and KO RBCs were preloaded with S1P in corresponding pHs in “preloading” assays. S1P release was stimulated by the addition of 0.5% bovine serum albumin. We noted that 0.5% bovine serum albumin used to capture S1P release in this assay strongly reduces the effect of CCCP. Therefore, we only observed the effects of CCCP with indicated concentrations. Data are expressed as mean and SD. n = 3 per genotype. Experiments were repeated twice. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. p Values were calculated using one-way ANOVA.