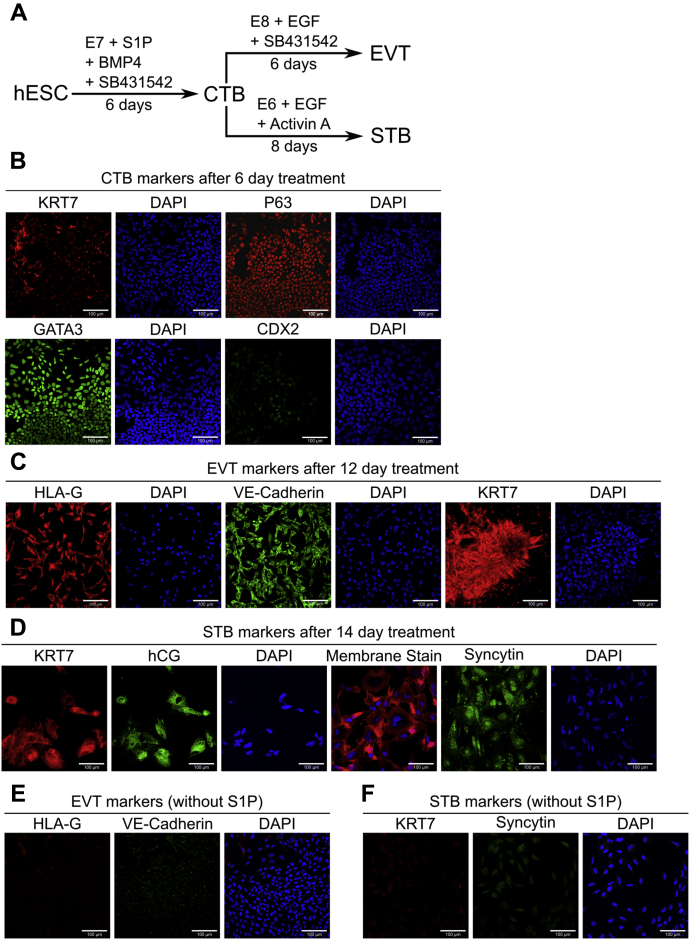
Figure 1.
A chemically defined medium containing S1P enables differentiation of hESCs to CTB-like cells and terminally differentiated trophoblasts.A, schematic of protocol for hESC differentiation to trophoblast. B, confocal images of CTB from 6-day initial treatment of H9 hESCs, staining for KRT7, P63, GATA3, and CDX2. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. C, confocal images of EVTs from 12-day treatment of H9 hESCs, staining for KRT7, HLA-G, and VE-Cadherin. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. D, confocal images of STB from 14-day treatment of H9 hESCs, staining for KRT7 and hCG, and syncytin. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Membrane was stained with CellMask deep red plasma membrane stain. E, confocal images of cells from 12-day EVT treatment of H9 hESCs upon removal of S1P, staining for HLA-G and VE-Cadherin. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. F, confocal images of cells from 14-day STB treatment of H9 hESCs upon removal of S1P, staining for KRT7 and syncytin. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. The scale bars represent 100 μm for all images. CTB, cytotrophoblast; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EVT, extravillous trophoblast; hESC, human embryonic stem cell; S1P, sphingosine-1 phosphate; STB, syncytiotrophoblast.