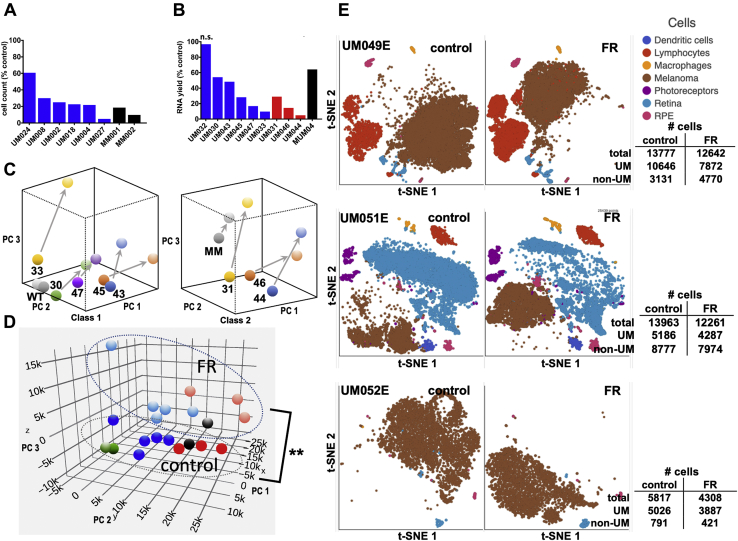
Figure 3.
Response of human UM tumor biopsy samples to FR ex vivo.A, effects of FR on cell abundance in self-renewing cultures from UM patient biopsies. Human tumor fine-needle biopsy samples of the indicated UM tumors were established in culture and split equally. Cells were counted after 7 days of culture upon treatment with vehicle or FR (100 nM). Each bar indicates an individual tumor sample. B, effect of FR on total RNA yield from UM patient biopsies. The indicated human UM biopsy samples from class 1 and class 2 primary UM tumors and a liver metastasis were dissociated, split equally, and treated immediately for 7 days with vehicle or FR (100 nM). The effect of FR relative to vehicle controls on the yield of total RNA as a marker of cell number is shown. Each bar indicates an individual tumor sample. One biopsy sample (UM032) expressed wildtype Gq and G11 and was unaffected by FR. In panels A and B, class 1 tumor samples are blue; class 2 tumor samples are red; metastatic tumor sample is gray. C, effect of FR on global gene expression in freshly isolated UM biopsies detected by RNAseq. Principal component analysis (PCA) of RNAseq data from class 1 (including the Gq/11-wild-type sample: WT) and class 2 (including metastatic sample: MM) human tumor biopsy samples. Arrows indicate the directional effect of FR on gene expression for each biopsy sample. D, combined PCA analysis of the effects of FR on gene expression in UM biopsy samples shown in panel C. Class 1 tumor samples are blue; class 2 tumor samples are red; metastatic tumor sample is gray; unresponsive wild-type Gq/G11 sample (UM032) is green. Correlations of principal component 1 (x-axis) and principal component 3 (z-axis) with FR-treatment were significant (paired t-tests with Holm–Šídák correction, p < 0.01: ∗∗). E, FR elicits transcriptional responses in UM tumor but not stromal cells as detected by single-cell RNAseq. Two-dimensional t-SNE plots of single-cell scRNAseq data are shown for each of the three indicated primary UM tumor samples obtained after enucleation, and treated 7 days with vehicle or FR (100 nM). Individual cell types are color coded in each panel. t-SNE plots of data obtained after vehicle (left panel) and FR (right panel) treatment of the indicated tumor samples are shown. The transcriptional profile of melanoma cells from a given tumor overlap little in vehicle- and FR-treated samples, indicating marked transcriptional response to FR. The transcriptional profile of each nonmelanoma cell type from a given tumor overlap extensively in vehicle- and FR-treated samples, indicating little transcriptional response to FR.