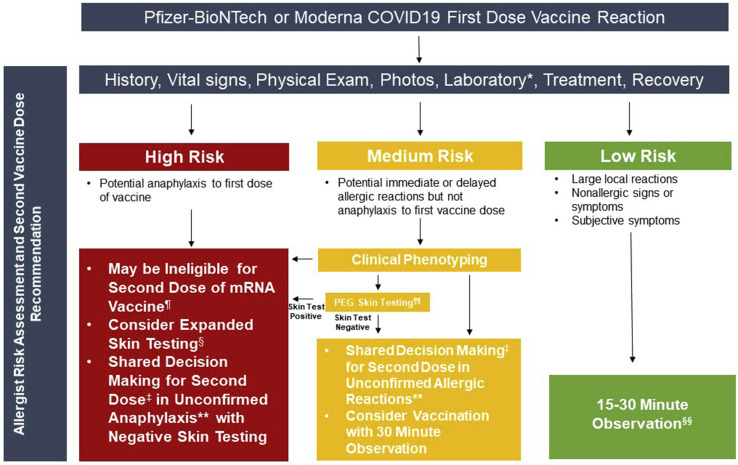
Figure 5.
Risk stratification pathways with categories based on Mass General Brigham and Vanderbilt allergy expert consensus after allergic reaction to first dose of COVID19 vaccine. ∗Ideal laboratory assessment includes reaction serum tryptase within 2 hours and complement activation by ELISA (C3a, C3b, C5a, C5b-9 ideally within 1 hour; send to National Jewish); follow-up baseline serum tryptase is also useful. ¶Follow CDC guidance.3 §See Figures 3 and 4 for expanded skin testing algorithm and nonirritating skin test concentrations. ‡Shared decision making with allergist considering eligibility for second dose or future challenge with other SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. There are no data on the safety of administering the second vaccine dose after potential anaphylaxis to the first dose and limited anecdotal evidence from the authors’ clinical experience suggesting that some patients can safely receive the second dose after more mild allergic type reactions to the first dose. If the decision is made to proceed with vaccination, staff should have anaphylaxis training and anaphylaxis kit needs to be available in close proximity. ∗∗84% (147/175) of potential anaphylaxis cases reported to the CDC were unconfirmed after their case review.2 ¶¶PEG skin testing can be considered to assist in the evaluation of a potential IgE mechanism but data confirming this mechanism is responsible for reported reactions to mRNA COVID-19 vaccines are lacking. §§Consider 15 or 30 minute observation based on clinical judgment.