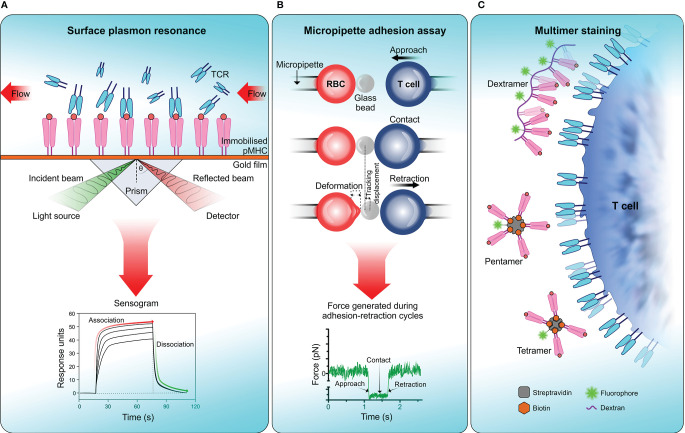
Figure 3.
Measuring TCR affinity . (A) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR). SPR measures the equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) of TCR-pMHC interactions in which pMHC is immobilized on a sensor surface and TCR molecules are injected in a continuous flow. Binding of TCR to pMHC results in a change of mass on the sensor surface and is recorded in a sensogram which is then used to calculate KD. (B) Micropipette adhesion assay. This technique uses two probes, one that is stationary which contains a red blood cell (RBC) attached to a functionalized glass bead to act as the adhesion force transducer and a mobile force probe bearing a T cell coupled to a piezotranslator. During adhesion-retraction cycles carried out by the mobile probe, the deformation of the RBC, displacement of the glass bead and the force generated in each cycle is recorded. (C) Multimer staining. This technique enhances the binding avidity of TCR-pMHC by increasing the valency of the interaction, results in more stable multimeric TCR-pMHC complexes for efficient labelling and detection. To date numerous forms of pMHC multimers have been reported which includes tetramers, pentamers, octamers, and dextramers (289).