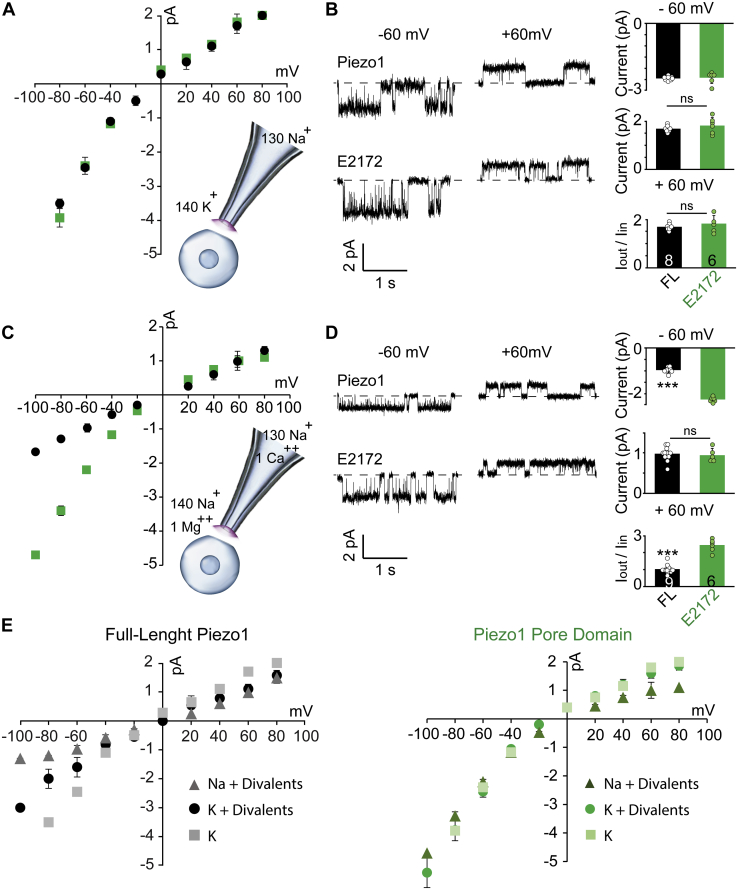
Figure 4.
Permeation properties of full-length Piezo1 and pore domain.A and C, the current–voltage relationships of full-length Piezo1 (black) and Piezo1 pore domain E2172 (green), The inset demonstrates ionic conditions to acquire data in an inside-out patch configuration: pipette and bath solutions do not contain divalent ions (n ≥ 5) (A), pipette and bath solutions contain Na+ with divalent ions (n ≥ 5) (C). B, left panel, single-channel current recordings in divalent-free solutions at ±60 mV. The dashed line represents closed state of the channel in each trace. B, right panel, single-channel current bar graphs at −60 mV (top), +60 mV (middle), and the Iout/Iin ratio at −60 mV/+60 mV (bottom). D, left panel, single-channel current recordings in symmetric Na+ solutions at ±60 mV. The dashed line represents closed state of the channel in each trace. D, right panel, single-channel current bar graphs at −60 mV (top), +60 mV (middle), and the Iout/Iin ratio at −60 mV/+60 mV (bottom). The data and statistics represented as Mean ± Standard Deviation, two-tailed t-test where ∗∗∗p < 0.0005. E, the single-channel current–voltage comparison of full-length Piezo1 and E2172 pore domain in various ionic conditions of the bath solution. The currents at each potential is represented as Mean ± Standard Deviation, where n > 6 experiments.