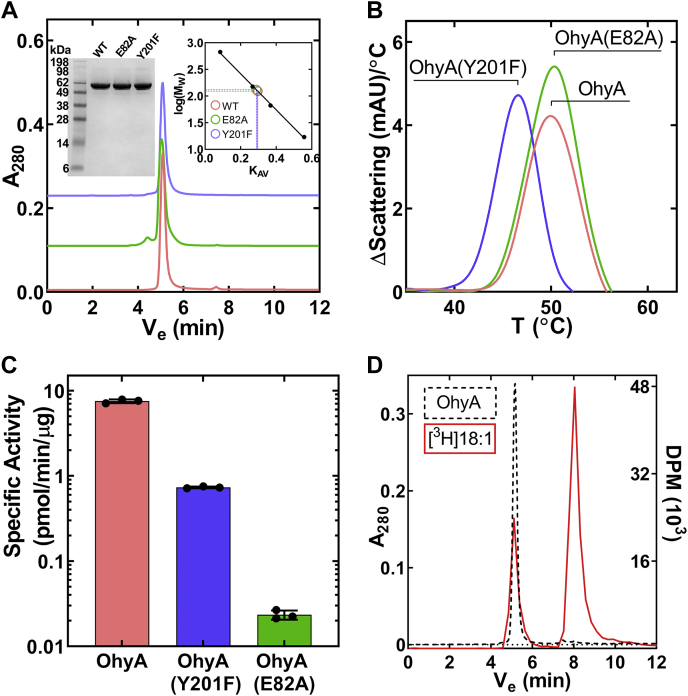
Figure 1.
Purification and properties of S. aureus OhyA and its mutant derivatives.A, Gel filtration chromatography of OhyA, OhyA(E82A), and OhyA(Y201F) indicates they are dimers. Left inset, SDS gel electrophoresis shows protein purity. Right inset, molecular weight calculation using calibration standards described in Experimental procedures. B, Representative first derivative plots of light scattering versus temperature for OhyA (48.2 °C ± 1.1 °C), OhyA(E82A) (49.0 °C ± 0.6 °C), and OhyA(Y201F) (45.6 °C ± 0.3 °C). Temperatures are reported as mean ± standard error (n = 3). C, Specific activities of OhyA (7.547 ± 0.221 pmol/min/μg), OhyA(Y201F) (0.735 ± 0.010 pmol/min/μg), and OhyA(E82A) (0.023 ± 0.03 pmol/min/μg). Specific activities are reported as mean ± standard error (n = 3). D, Gel filtration chromatogram shows OhyA binds [3H]oleate in the absence of FAD. OhyA was monitored by A280 (dashed black line) and [3H]oleate was monitored by scintillation counting (DPM) (red line). FAD, flavin adenine dinucleotide; OhyA, oleate hydratase.