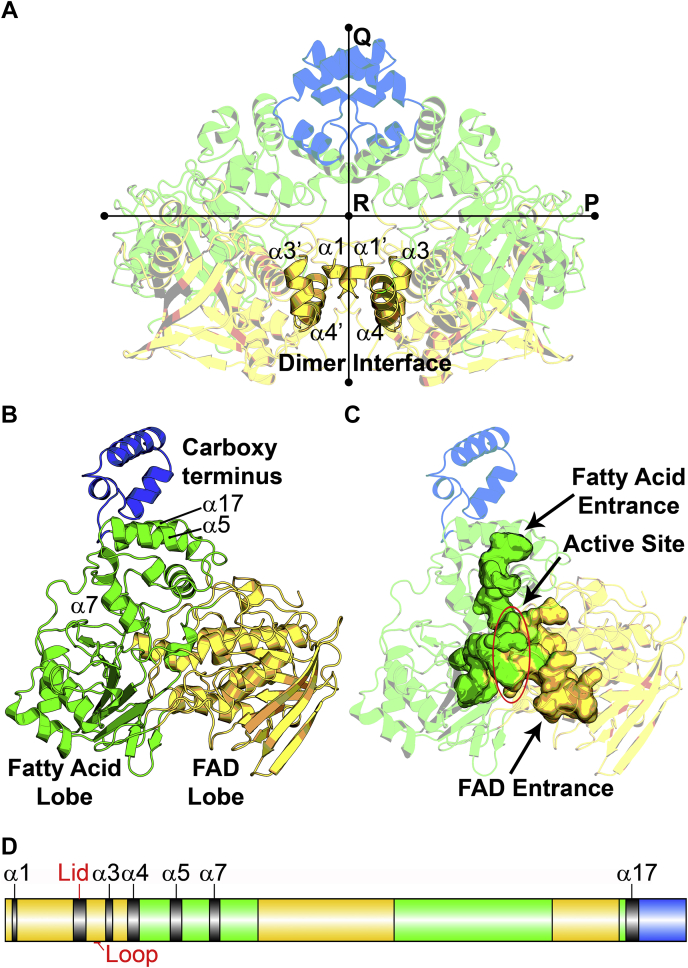
Figure 2.
OhyA is a dimer composed of three functional domains. The fatty acid lobes are green, FAD lobes are yellow, and carboxy termini are blue. A, OhyA proteins use interacting helices α1, α3, and α4 to form the OhyA dimer interface along the Q axis. B, The OhyA protomer is divided into three functional domains: FAD lobe, fatty acid lobe, and carboxy terminus. C, The interior cavity of an OhyA protomer is mapped in solid color showing the contributions of the fatty acid (green) and FAD (yellow) lobes. Fatty acids enter the hydrophobic tunnel just below the carboxy terminus and FAD enters through the FAD lid at the opposite end. The active site is located at the intersection of the fatty acid and FAD cavities. D, The functional domains are mapped onto the primary sequence. The locations of key α helices, the sequence the covers FAD (Lid), and the active site loop (Loop) are indicated. FAD, flavin adenine dinucleotide; OhyA, oleate hydratase.