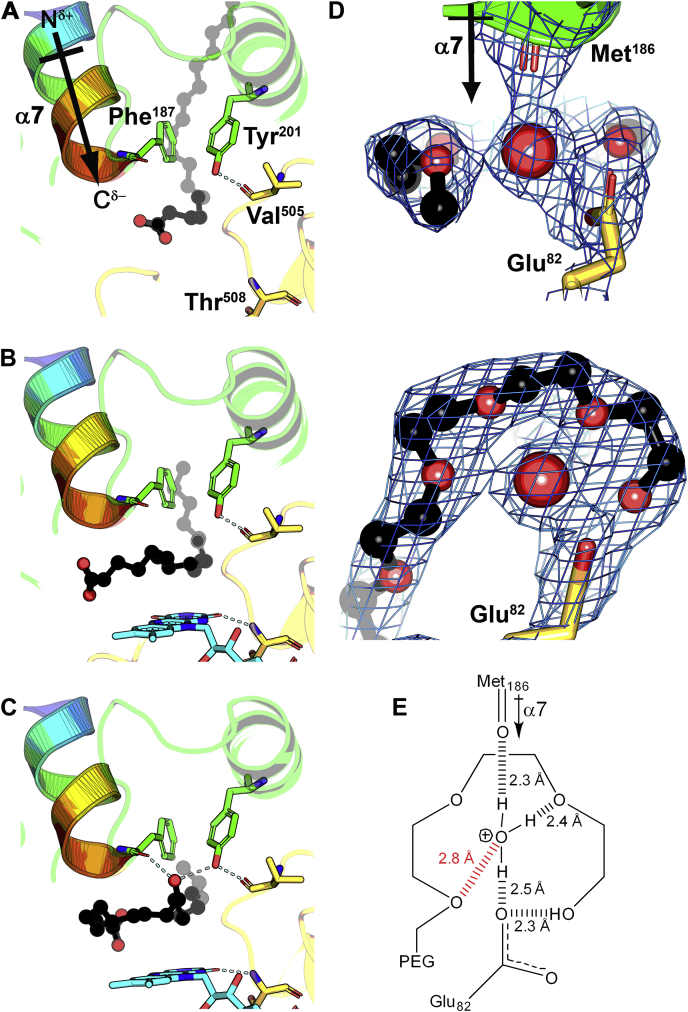
Figure 8.
Role of Tyr201 and the hydronium ion. Contributions from the FAD lobe are yellow, fatty acid lobe is green, fatty acid is black, and FAD is cyan. A, The OhyA(E82A)•oleate complex (PDB: 7KAZ, MolA) shows the α7 helix dipole colored from blue (amino terminus) to red (carboxy terminus). Tyr201 on the fatty acid lobe makes a 2.7 Å hydrogen bond interaction with the carbonyl of Val505 on the FAD lobe to seal one side of the active site. B, The OhyA(E82A)•oleate•FAD complex (PDB: 7KAZ, MolB) shows the oleate chain rotating into the active site above FAD making van der Waals contact with the hydrophobic xylene ring. C, The OhyA(E82A)•h18:0•FAD product complex (PDB: 7KAZ, MolC) shows the Phe187 backbone carbonyl-product hydroxyl-Tyr201 hydroxyl-Val505 backbone carbonyl hydrogen bond network that stabilizes water addition to carbon-10 of the fatty acid. D, Two rotated snapshots of the coordination network show three direct interactions with contiguous electron density to the catalytic water molecule (red sphere). An interaction between Glu82 and the PEG400 terminal hydroxyl is evident. Electron density calculated from a 2mFO − DFC map contoured at 1 σ (blue mesh). E, Diagram of the hydrogen bonding network surrounding the substrate water. Distances represent measurements between oxygen atoms are shown with three hydrogen bonds connected to the water oxygen indicating it is a positively charged hydronium ion. FAD, flavin adenine dinucleotide; OhyA, oleate hydratase; PEG400, polyethylene glycol 400; h18:0, (R)-10-hydroxyoctadecanoic acid.