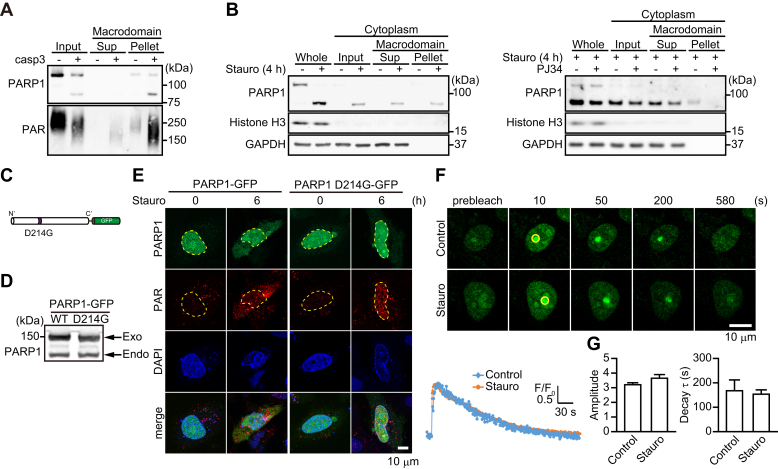
Figure 4.
89-kDa PARP1 fragments were translocated to the cytoplasm with attached PAR.A, GST pull-down assay using GST macrodomain. Recombinant human PARP1 proteins automodified by PAR were incubated with recombinant human caspase-3 proteins for 4 h. GST pull-down assay using GST macrodomain was used to isolate poly(ADP-ribosyl)ated proteins. B, poly(ADP-ribosyl)ated 89-kDa PARP1 fragments in the cytoplasm. HeLa cells were exposed to 300 nM staurosporine for 4 h (left) without or with PJ34 (10 μM) (right). After subcellular fractionation, cytoplasmic fractions were subjected to GST pull-down assay using GST macrodomain. Histone H3 and GAPDH were used as nuclear and cytoplasmic markers, respectively. C, schematic diagram of PARP1 D214G-GFP construct. D, PARP1-GFP WT and D214G expression in HeLa cells. After 1-day transfection, Western blotting using anti-PARP1 antibody was performed to confirm expression. The lower arrow indicates endogenous PARP1 expression in HeLa cells, whereas the upper arrow shows exogenous PARP1 expression. E, localization of PARP1 D214G-GFP and PAR after 6-h exposure to staurosporine (300 nM). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Yellow lines indicate the position of nuclei. The scale bar represents 10 μm. F, effect of caspase activation on the recruitment of PARP1 D214G to DNA lesions induced by microirradiation with 2-h exposure to staurosporine (300 nM). Cells transiently transfected with PARP1 D214G-GFP were subjected to microirradiation without or with 300 nM staurosporine at the indicated circle. The scale bar represents 10 μm. Right graphs indicate the time course of fluorescence of PARP1 D214G at circles. Images were taken every 2 s for 10 min. G, effect of caspase activation on the mean amplitude (left) and decay time constant (right) of PARP1 D214G-GFP after microirradiation without or with 300 nM staurosporine (means ± S.E.M., n = 8) versus control (Student's t test). DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; PAR, poly(ADP-ribose); PARP1, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; WT, wild-type.