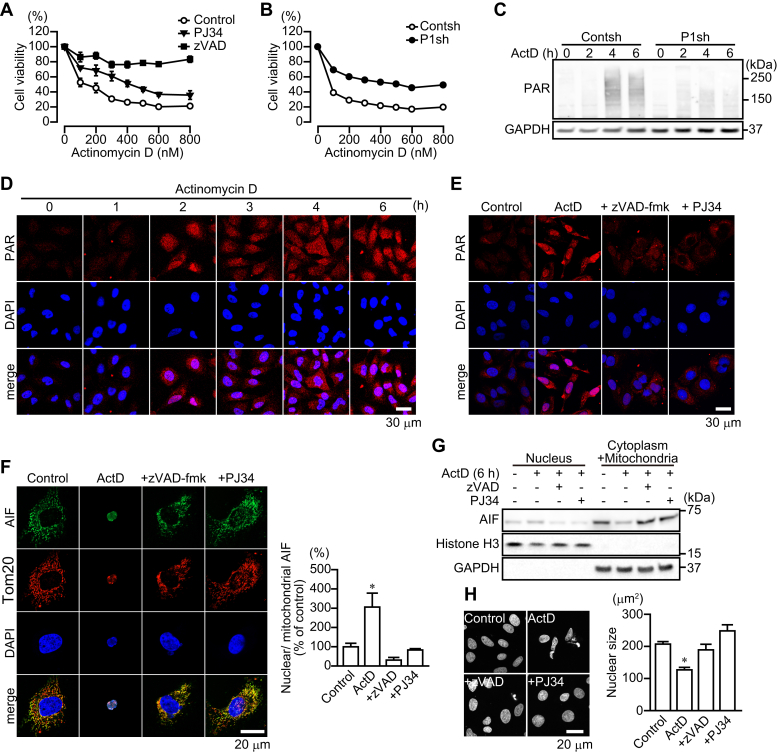
Figure 6.
PARP1-mediated AIF release after caspase activation after actinomycin D exposure.A, actinomycin D-induced cell death. HeLa cells were exposed to actinomycin D (12 h) at indicated concentrations. zVAD-fmk (50 μM) or PJ34 (10 μM) was added for 30 min before actinomycin D exposure (means ± S.E.M., n = 3). ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus control at above 200 nM (two-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test). B, effect of PARP1 depletion on actinomycin D-induced cell death (means ± S.E.M., n = 3). HeLa cells stably expressing control or PARP1 shRNA were exposed to actinomycin D for 24 h before assessment of cell viability. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus control at above 100 nM (two-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test). C, time course of PAR synthesis after actinomycin D exposure. After exposure to actinomycin D (300 nM) for indicated times, HeLa cells stably expressing control and PARP1 shRNAs were subjected to Western blotting using anti-PAR antibody. GAPDH was used for a loading control. D, time course of PAR localization after actinomycin D exposure. After exposure to actinomycin D (300 nM) for indicated times, cells were subjected to immunocytochemistry using anti-PAR antibody (red). DAPI was used as a nuclear marker. E, effect of caspase and PARP inhibition on PAR localization. zVAD-fmk (50 μM) or PJ34 (10 μM) was added before actinomycin D (300 nM) exposure. HeLa cells were subjected to immunocytochemistry using anti-PAR antibody (green). DAPI was used as a nuclear marker. The scale bar represents 30 μm. F, AIF accumulation in nuclei of HeLa cells after 6-h exposure to actinomycin D. Cells were subjected to immunocytochemistry using anti-AIF antibody(green), anti-Tom20 antibody (red), and DAPI staining (blue). The scale bar represents 20 μm. Right graph shows the ratio of nuclear to mitochondrial AIF fluorescence. (means ± S.E.M., n = 3). ∗p < 0.05 versus control (one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test). G, AIF localization in nuclei. After 6-h exposure to actinomycin D (300 nM), nuclear and cytoplasmic/mitochondrial fractions were separated. zVAD-fmk (50 μM) or PJ34 (10 μM) was added for 30 min before staurosporine exposure. Histone H3 and GAPDH were used as nuclear and cytoplasmic markers, respectively. H, nuclear shrinkage after 6-h exposure to actinomycin D. After exposure to actinomycin D (300 nM), DAPI was used to measure nuclear sizes in HeLa cells. The scale bar represents 20 μm. Right graph shows mean nuclear sizes (means ± S.E.M., n = 100–300 cells). ∗p < 0.05 versus control (one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test). DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; PAR, poly(ADP-ribose).