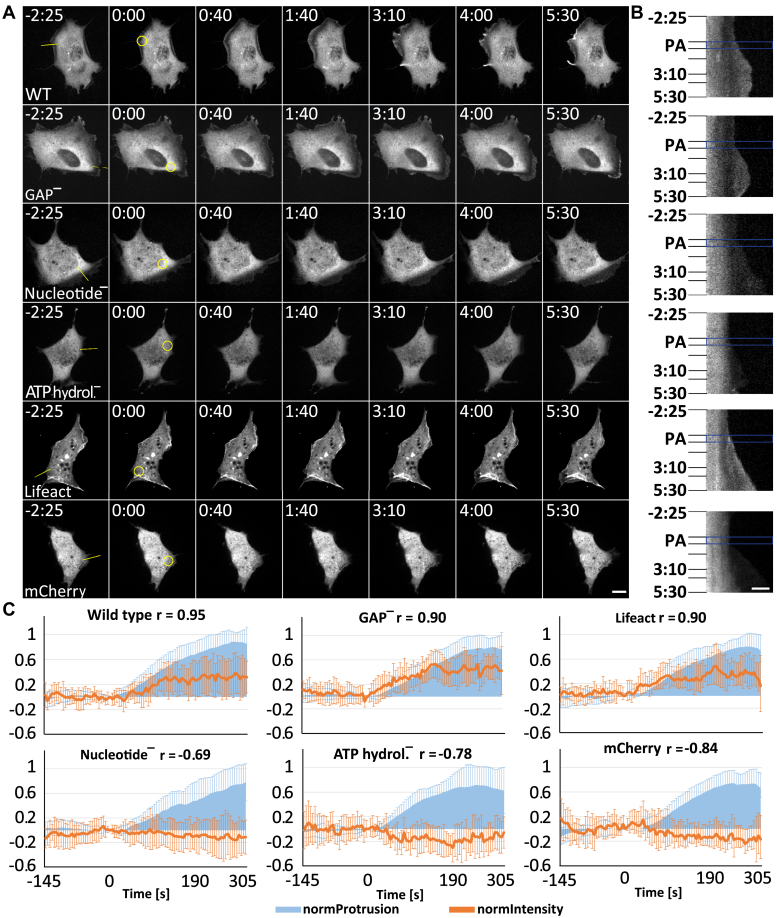
Figure 1.
Myo9b accumulates at the leading edge of Rac-induced protrusions.A–B, NIH/3T3 cells coexpressing PA-Rac and mCherry-Myo9b (WT), mCherry-Myo9bR1695M (GAP−), mCherry-Myo9bG244R (nucleotide−), mCherry-Myo9bR295C (ATP hydrol.−), Lifeact-mRFPruby, or mCherry were analyzed by live cell fluorescence microscopy. A time-lapse movie monitoring the distribution of Myo9b and control constructs was recorded with a frame rate of 5 s on a spinning disc microscope. Starting after 30 frames (145 s), PA-Rac was activated in the indicated ROI (A, yellow circle in the second images from the left) by irradiation with 405-nm light using a FRAP module. Photoactivation was repeated every 5 s for a total of 35 s, and the reaction of the cell was monitored until several minutes afterward. A, single images from a characteristic time-lapse movie. Time stamp indicates the time relative to photoactivation onset. The cell forms a protrusion in response to the photoactivation that persists for several minutes after photoactivation. Myo9bWT and Myo9bGAP− accumulated at the leading edge of this protrusion. Myo9bWT accumulated additionally in an actin comet tail. Scale bar, 15 μm. B, kymographs of the movies to the left in A recorded along the line indicated in yellow in the first image of A. PA (blue rectangle) indicates the photoactivation phase. Time points of the single images shown in A are indicated to the left. Scale bar, 5 μm. C, averaged normalized protrusions (light blue) and corresponding construct intensities at the leading edge (brown lines) are plotted. Time 0 indicates the start of Rac photoactivation. For each construct, n = 10 independent photoactivation experiments. Error bars represent standard deviations. Wild type: mCherry-Myo9b wild type; GAP−: mCherry-Myo9b R1695M (GAP-inactive mutant); Lifeact: Lifeact-mRFPruby; Nucleotide−: mCherry-Myo9b G244R (motor mutant); ATP hydrol.−: mCherry-Myo9b R295C (motor mutant); mCherry: mCherry-tag only.