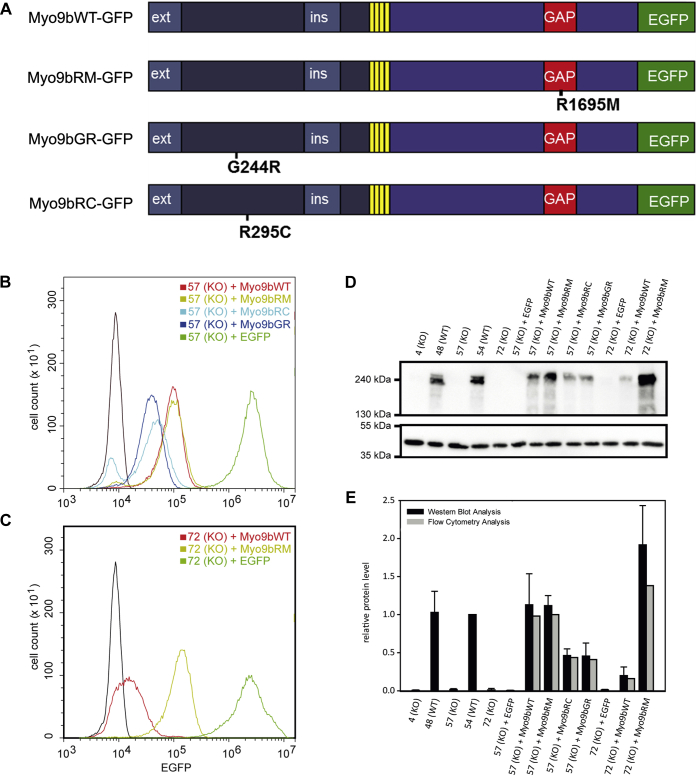
Figure 6.
Generation of Myo9b-deficient cell clones that express different recombinant Myo9b constructs. Different Myo9b constructs were designed as shown schematically in A. Stable HL-60 cell lines were generated by lentiviral transduction of two independent Myo9b knockout clones with Myo9b WT, Myo9bGAP− (Myo9bRM), and EGFP and a single Myo9b knockout clone with the two different Myo9b motor mutants nucleotide− (Myo9bGR) and ATP hydrol− (Myo9bRC). B–C, analysis of the expression of recombinant Myo9b-EGFP fusion constructs in cell lines derived from the Myo9b-deficient cell clone 57 (B) and clone 72 (C) by flow cytometry. D, an immunoblot of cell homogenates is shown demonstrating the expression of the indicated Myo9b constructs. For comparison, cell homogenates of the two wild type–like clones #48 and #54 were also probed. β-Actin served as a loading control. All recombinant Myo9b constructs had EGFP fused to their C-terminus. E, quantification of the expression levels of endogenous Myo9b and the different Myo9b constructs in the different cell lines. Expression was quantified using immunoblots and for the recombinant Myo9b-EGFP constructs in addition flow cytometry. Levels of Myo9b expression were normalized to either endogenous Myo9b of clone 54 or recombinant Myo9bWT in clone 57. n = 3, mean ± SD.