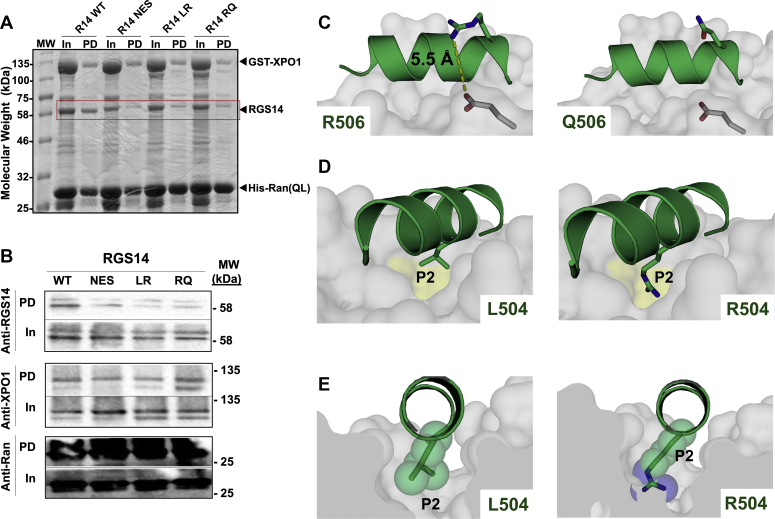
Figure 6.
Human variants LR and RQ disrupt RGS14 binding to Exportin 1 (XPO1) through loss of side-chain interactions.A–B, recombinant RGS14 WT and variants LR and RQ were purified from E. coli and mixed with purified GST-XPO1 and constitutively active His-Ran (GV)-GTP. His-Ran (G/V)-GTP was captured by Ni-NTA affinity pull-down and complexes were assessed by Coomassie (A) and immunoblot (B). WT RGS14 was recovered in complex with XPO1, but RGS14 NES, RGS14 LR, and RGS14 RQ did not bind XPO1. Blots are representative of five independent experiments. C, structural modeling of the R506Q variant binding to XPO1. Left panel is the wild-type amino acid, arginine, which makes a salt bridge with a nearby glutamate near the binding pocket on XPO1. Mutation to a glutamine (right panel) removes this salt bridge, presumably destabilizing the protein–protein interaction. D–E, structural modeling of the L504R variant onto XPO1. The leucine interacts directly with the hydrophobic P2 pocket (left panel). Mutation of this amino acid to an arginine (right panel) introduces a charged side chain into a hydrophobic pocket. These data mechanistically explain the difference in phenotype (R506Q being a subtler phenotype compared with L504R).