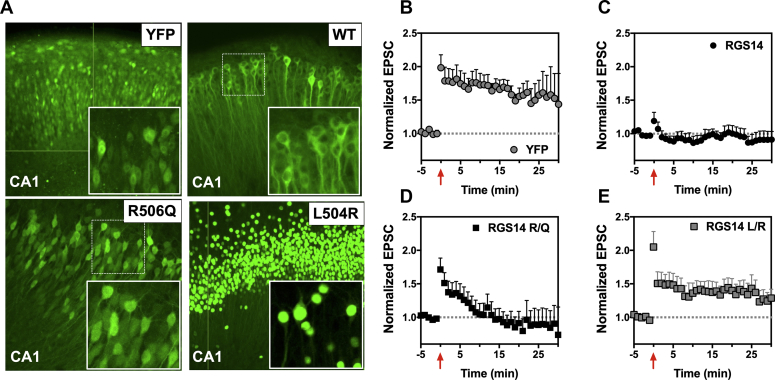
Figure 7.
Human variants LR and RQ that disrupt RGS14 nuclear-cytoplasmic equilibrium also block RGS14 capacity to inhibit long-term potentiation in hippocampal slices. AAV-eYFP-RGS14 was used to make AAV2/9 viruses, including wild-type RGS14 as well as human variants RQ and LR. Furthermore, a stop codon was generated as follows AAV-YFP-STOP-RGS14, to make a truncated YFP virus lacking RGS14. Virus was injected into mouse CA1 slice cultures and incubated for 1 week, at which point electrophysiological recordings were made to assess LTP. A, expression of YFP-RGS14 in CA1 brain slices. To improve visualization of individual neurons, insets are shown derived from cutout white dashed boxes (WT and R506Q) or as 20× images where individual cell resolution in the cutout was not sufficient (YFP and L504R). The horizontal and vertical green lines in images for YFP and L504R represent the interface where composite confocal images were spliced together. WT RGS14 fills the cytoplasm of neurons. RQ fills both the cytoplasm and nucleus, while LR localizes predominantly to the nucleus, entirely consistent with our data in dissociated neurons. Images are representative of 6 to 9 experiments. B–E, long-term potentiation (LTP) was induced by an LTP pairing protocol in CA1. YFP alone (n = 8) had no effect on LTP, but in contrast, WT RGS14 (n = 6) completely inhibits LTP in CA1, a hippocampal region where RGS14 is not natively found. Potentiation lasting only about 10 min was induced in RQ variant-expressing neurons (n = 9), whereas the LR variant (n = 9) failed to suppress LTP. ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc analysis demonstrated a statistically significant difference between YFP alone (control) and WT RGS14 at 5 (p = 0.03) and 10 (p = 0.006) min poststimulation, while RGS14 LR was not statistically different from YFP alone at either time point. RGS14 RQ was statistically different from YFP alone at 10 min poststimulation (p = 0.018), but not 5 min. This suggests that the degree of mislocalization by these variants correlates with ablation of RGS14 function in CA1 neurons. Data is presented as mean ± SEM.