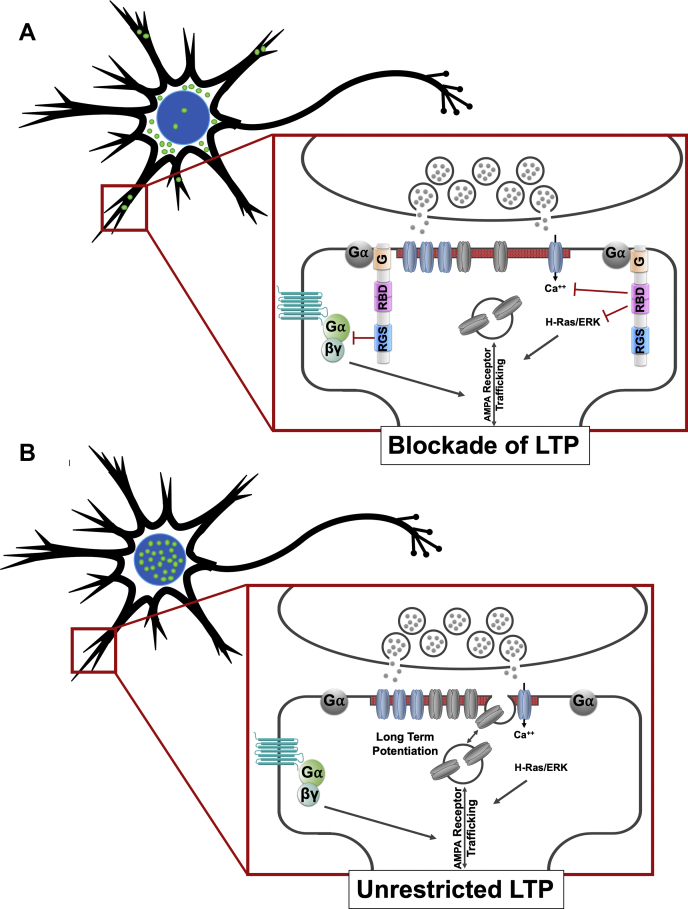
Figure 9.
Proposed working model of RGS14 spatial-dependent inhibition of LTP.A, wild-type RGS14 (green dot) is disperse throughout the neuron, occupying multiple compartments including the nucleus, the cytoplasm, and the dendrites and spines (red box). Within a dendritic spine (expanded red box), Gα-GDP interaction with the G protein regulatory motif (G) brings RGS14 to the microcompartment necessary for inhibition of GPCR signaling by the RGS domain, inhibition of H-Ras/ERK signaling by the Ras binding domains (RBD), and inhibition of Ca++ signaling, all of which support LTP in the absence of RGS14. B, variant forms of RGS14 (green dots) are sequestered in the nucleus and cannot reach dendrites (red box). Due to their mislocalization, they cannot interact with, and be recruited by, Gα-GDP to dendritic compartments (expanded red box). The lack of RGS14 at these microcompartments allows for unrestricted GPCR, H-Ras/ERK, and Ca++ signaling, removing the block on LTP.