Figure 4.
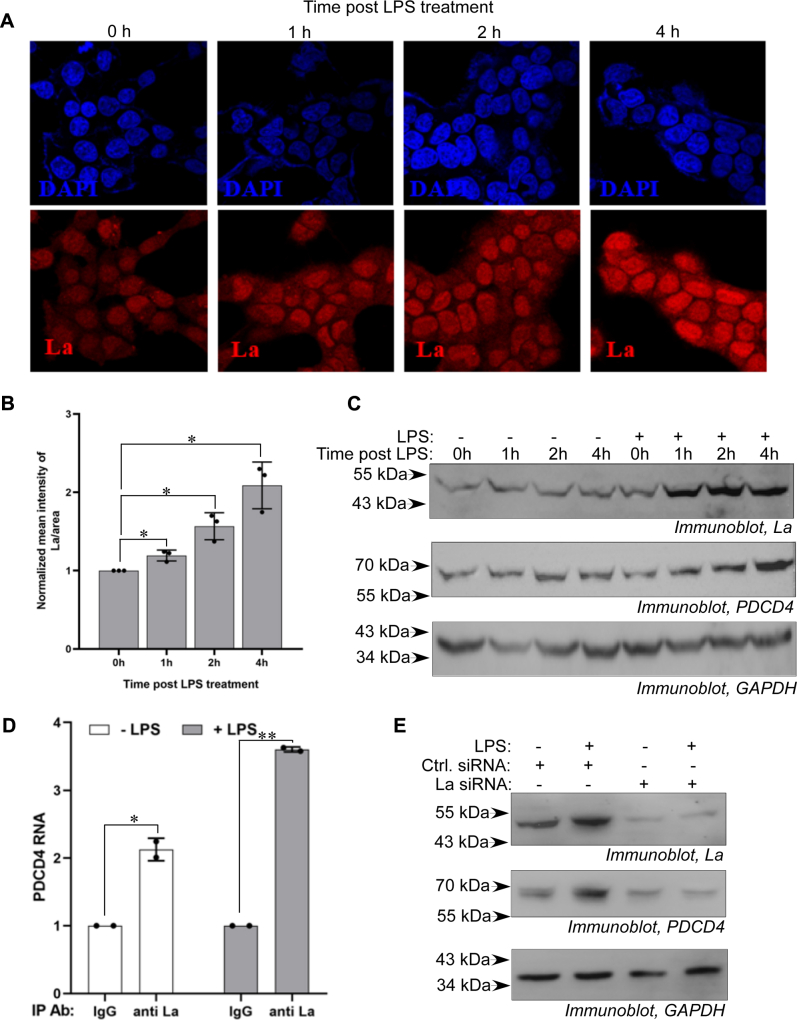
LPS treatment induces La protein level and enhances PDCD4 expression. A, MCF7 cells were treated with LPS (500 ng/ml), and immunofluorescence of cells collected at various time points after LPS treatment was observed using anti-La primary and AlexaFluor 568-conjugated secondary antibody (red). Nucleus was visualized using DAPI staining (blue). B, fluorescence intensity/cell of three random fields from each time-point after LPS treatment was determined and normalized to 0 h time point and plotted. The data represent mean fluorescence intensities ±SD from three independent experiments. ∗ represents significant difference (p-value ≤ 0.05) from 0 h LPS-treated cells. C, immunoblots of cytoplasmic lysates of MCF7 cells treated without/with LPS (500 ng/ml) and collected at different time-points posttreatment probed with anti-La, anti-PDCD4, and anti-GAPDH antibodies. D, cytoplasmic lysates of MCF7 cells treated with/without (500 ng/ml) LPS for 4 h were immunoprecipitated with La antibody or control IgG. mRNA associated with the immunoprecipitates was subjected to qRT–PCR using PDCD4 or β-actin primers. PDCD4 mRNA level was normalized to β-actin mRNA level. The data represent fold excess of normalized PDCD4 mRNA in La immunoprecipitate over IgG immunoprecipitate. ∗ and ∗∗Represents significant difference (p-value ≤ 0.05 and ≤0.01 respectively) from respective IgG immunoprecipitate controls. E, immunoblots of lysates from MCF7 cells transfected with La siRNA or control siRNA (50 pmole) and treated with LPS for 4 h, probed with PDCD4, La and GAPDH antibodies. La, lupus antigen; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PDCD4, programmed cell death 4.