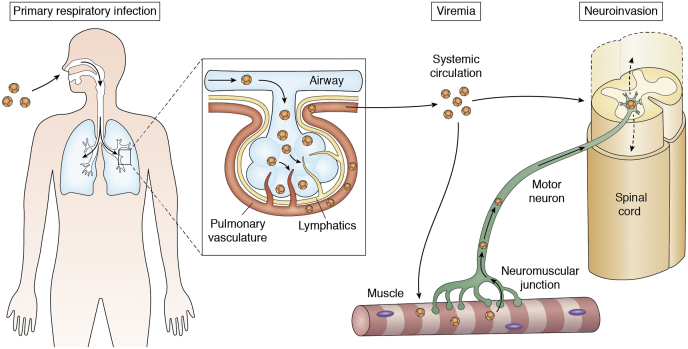
Figure 4.
Hypothesized mechanisms of neuroinvasion. Enterovirus D68 (EV-D68) is primarily transmitted as a respiratory infection. In a subset of patients, EV-D68 may translocate into the blood stream to establish viremia. The pathway might involve direct entry into the circulation or like poliovirus may occur first via the lymphatic system. After establishing systemic circulation, EV-D68 may enter the central nervous system in one of two ways: (1) direct hematogenous seeding or (2) replication in muscle fibers followed by translocation across the neuromuscular junction and retrograde transport within the motor axon. EV-D68 then likely continues to spread within the spinal cord.