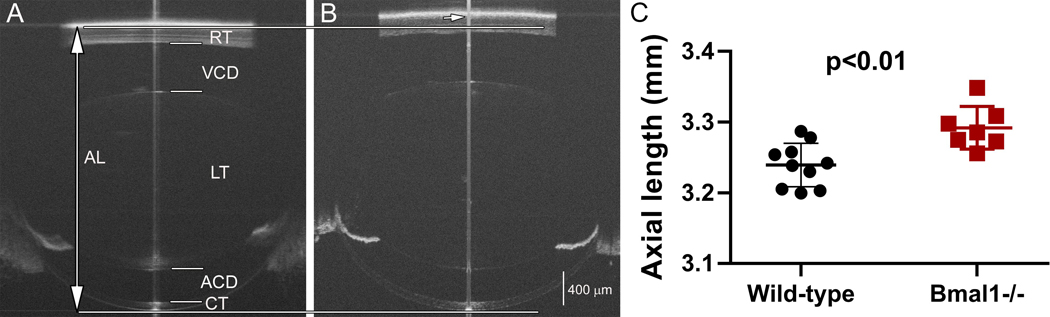
Figure 6: Using SD-OCT to evaluate axial length in a mouse model of myopia.
Whole eye SD-OCT images of wild-type (A) and Bmal1−/− (B) mouse eyes at 84 days of age. The eyes of Bmal1−/− mice have significantly longer axial length than the wild-type eyes (C). AL: axial length; RT: retinal thickness; VCD: vitreous chamber depth; LT: lens thickness; ACD: anterior chamber depth; CT: corneal thickness. The long vertical line indicates axial length boundaries (top and bottom indicated by horizontal line) for the wild-type eye. Short arrow indicates the posterior axial length marking for the Bmal1−/− eye. Mean ± SEM. (Note: The central line down the middle of each image (A&B) is a vertical saturation artifact. It is typically used as a guide to center the eye, but if the scan is well aligned, it can be made to disappear.)