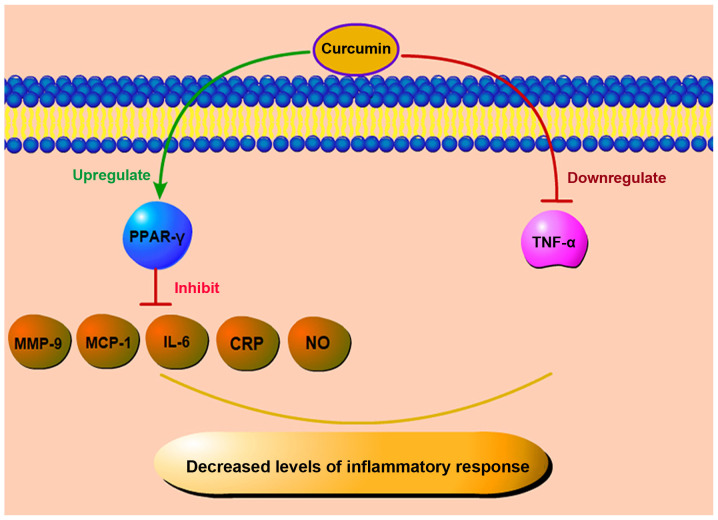
Figure 4.
Anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin. Curcumin controls inflammatory responses by reducing inflammatory factors, such as MCP-1, IL-6, MMP-9, NO, and CRP, upregulating the level of PPAR-γ, and downregulating TNF-α. MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; IL-6, interleukin-6; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; CRP, C-reactive protein; NO, Nitric oxide; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-γ; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α.